The Impact of Digitalization on Shipbuilding as Measured by Artificial Intelligence (AI) Maturity Models: a Systematic Review
Volume 10, Issue 3, Page No 15–20, 2025
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 10(3), 15–20 (2025);
 DOI: 10.25046/aj100303
DOI: 10.25046/aj100303
Keywords: Digitalization, Shipping, Transformation, Technologies, Maturity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the global shipbuilding sector, yet existing maturity models fail to capture the domain-specific complexities of this capital-intensive industry. This study reviews over 50 AI maturity models and introduces a specialized framework tailored for shipbuilding. The proposed model outlines four progressive stages—Beginner, Innovation, Integration, and Expert—across eight key dimensions: culture, resilience, sustainability, strategy, customer focus, organizational integration, connectivity, and production efficiency. A hybrid benchmarking approach involving comparative analysis of major shipbuilders such as China State Shipbuilding Corporation(CSSC), General Dynamics National Steel and Shipbuilding Company(NASSCO), and Hyundai Heavy Industries(HHI), as well as synthesis from literature, was used to validate the relevance and coverage of each dimension. The framework provides a roadmap for operational modernization and links digital maturity to measurable outcomes such as delivery timelines, production scalability, and environmental performance. Policy recommendations highlight the need for targeted investments, workforce reskilling, and public-private collaboration to enable sustainable and AI-enabled growth in the U.S. shipbuilding sector.
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is redefining industrial processes globally, with the shipbuilding sector increasingly adopting AI to improve efficiency, safety, and competitiveness [1]. Nations such as China, South Korea, and Japan dominate the global shipbuilding landscape due to superior infrastructure, automation, and AI-driven capabilities [2].
Training shipyard workers in modern shipbuilding techniques and using AI will be imperative for global shipyards [3]. Organizations must understand and adapt artificial intelligence to specific uses and requirements[4]. Real-time decision-making relies on statistics, econometrics, math, simulations, and optimization to collect and analyze high-speed data from multiple sources [5]. Using current and new web data can assist organizations in identifying their competitors [6]. The Chinese shipyards enjoy state-of-the-art infrastructure, automation, and government subsidies, allowing them to reach economies of scale and construct multiple ships simultaneously [7]. China State Shipbuilding Corporation, the world’s largest shipbuilding conglomerate, now owns numerous research institutes and various shipyards and builds a third of all ships worldwide. Government and shipyards work closely together to achieve their national strategic goal of being a world leader in the maritime industry [7].
The shipbuilding industry remains a vital contributor to national economies, particularly in the United States, where the sector supports over 100,000 jobs, generates $9.9 billion in labor income, and contributes $12.2 billion to GDP annually [4]. However, despite its strategic significance, the U.S. shipbuilding sector has significant obstacles that limit its capacity to compete internationally, such as aging infrastructure, high labor costs, and a shortage of people with digital skills [8], [9]. Conversely, shipyards in China and South Korea enjoy substantial government backing, cutting-edge automation, and state-sponsored training programs, which allow them to increase production capacity and swiftly incorporate AI technologies [8]. As noted by the World Bank, the availability of a skilled labor force and policies promoting industrial transformation are key enablers of digital readiness and economic resilience in heavy industries [8]. These contrasts underscore the urgency for targeted digitalization strategies in U.S. shipyards, where AI maturity assessments can help guide sustainable modernization efforts [10].
The adoption of automation and artificial intelligence in shipbuilding can result in cost reductions, enhanced safety, and faster production cycles [11]. However, this transformation varies across regions. Chinese shipyards have rapidly embraced AI-powered robotics and analytics, whereas their U.S. counterparts continue to rely on conventional systems that prioritize operational resilience [7].
This paper aims to summarize and evaluate existing AI maturity models, assess the digitalization levels of leading shipbuilding nations, identify gaps in current AI maturity assessment frameworks as they apply to the shipbuilding industry, and propose a specialized AI maturity model tailored to address the sector’s unique challenges and characteristics.
This paper evaluates how digitalization influences shipbuilding outcomes, using AI maturity models as the assessment tool. Our research objectives are:
- To review global AI maturity models applicable to manufacturing and maritime sectors.
- To identify limitations in existing frameworks when applied to shipbuilding.
- To propose and validate a tailored AI maturity model for shipbuilding.
- To assess how AI maturity affects efficiency, delivery timelines, and sustainability.
By answering research questions related to AI maturity’s role in digital transformation, model effectiveness, and comparative insights, we provide a strategic lens for shipbuilding modernization.
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Foundation
We reviewed 50 scholarly sources across IEEE, Springer, ACM, and ScienceDirect databases using Boolean keywords (“AI maturity model,” “shipbuilding,” “digital transformation”). The review found that existing models, such as the Digital Maturity Model (DMM) [12], [13], Global Big Data Maturity Model (GBDMM) [14], do not adequately reflect the shipbuilding sector’s complexity.
Key dimensions such as resilience, sustainability, and connectivity are inconsistently applied. Moreover, few models account for shipbuilding’s unique regulatory, infrastructural, and labor requirements. These dimensions can be used to quantitatively evaluate an organization’s AI adoption maturity practices, providing a comprehensive framework for qualitatively evaluating and improving AI adoption maturity practices. Table 1 shows the dimensions of the available maturity models, and Figure 1 shows AI dimensions.
Table 1: Dimensions in Existing AI Maturity Models
| Dimension | [15] | [16] | [17] | [18] | [19] | [20] | [21] | [22] | [23] | [14] |
| Culture | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Resilience | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Sustainability | X | X | ||||||||
| Strategy | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Customer | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Organization | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Connectivity | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Expansive Growth | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Production | X | X | X | X | X |
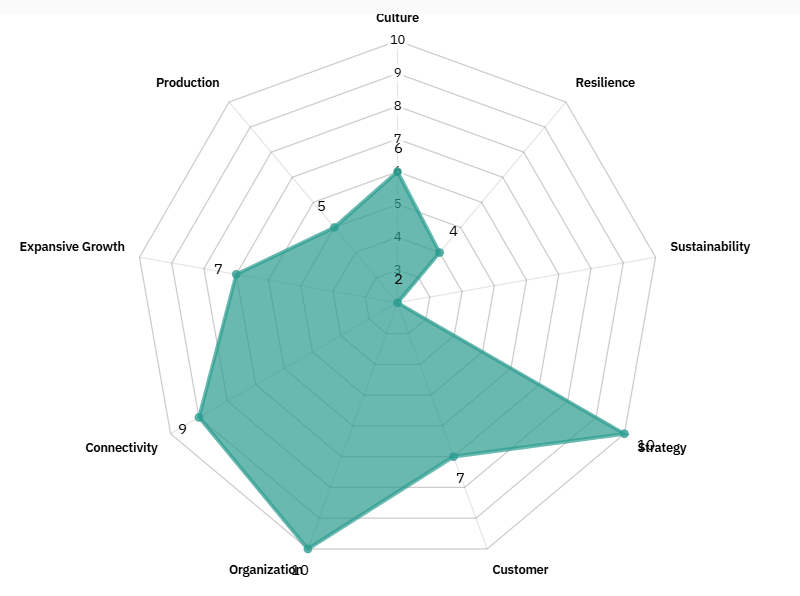
Note: The AI dimensions above are derived from the table and referenced models. This comparison highlights inconsistencies in how different models address key elements relevant to digital transformation in complex industries such as shipbuilding.
3. Comparative Case Study: U.S. vs. China
U.S. Shipbuilding:
- General Dynamics NASSCO focuses on defense contracts, producing 2–3 vessels per year [24].
- 2023 revenue (Marine Systems): $12.5B [24].
- Constraints: high labor costs, limited automation, reliance on military demand [25].
China Shipbuilding:
- China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC) constructs ~33% of global ships [26].
- Backed by government subsidies, high R&D, and integrated AI systems [26].
Table 2 presents the annual turnover figures (in USD billions) for four major shipbuilding organizations from 2019 to 2023. China’s CSSC shows a steady rise in turnover, from approximately $7.19 billion in 2019 to around $10.77 billion in 2023, reflecting its expanding global presence and state-backed initiatives. South Korea’s HD Hyundai Heavy Industries (HD HHI) maintains moderate growth, with revenue climbing from $7.12 billion in 2019 to $9.2 billion in 2023. In contrast, Japan’s Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) exhibits relative stability, with turnover fluctuating slightly between $1.42 and $1.67 billion, indicating a more consistent but less expansive market footprint than its peers.
Table 2: Annual Turnover (USD Billion)
| Year | General Dynamics* | CSSC** | HD HHI*** | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (MHI)**** |
| 2023 | 42.3 | ~10.77 | 9.2 | 1.42 |
| 2022 | 39.4 | ~8.14 | 7.05 | 1.42 |
| 2021 | 38.5 | ~8.16 | 7.25 | 1.50 |
| 2020 | 37.9 | ~7.55 | 7.03 | 1.67 |
| 2019 | 39.4 | ~7.19 | 7.12 | 1.66 |
*General Dynamics’ total revenue includes revenue from other segments, including NASSCO. NASSCO does not disclose figures annually, but they are included in the segment’s operations [24], [25]
**In 2019, China State Shipbuilding Industry Corporation and China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation merged, significantly boosting revenue for CSSC [26]
***HD Hyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. (HHI) is a leading shipbuilding company based in Ulsan, South Korea [27]
****Historically, shipbuilding & ocean development have contributed approximately 3%–6% to MHI’s total revenue [28]
4. Gaps in Existing AI Maturity Models
Most maturity models:
- Use generic stages (e.g., planning, integration, optimization)
- Lack of empirical application in the shipbuilding context
- Do not align AI dimensions with shipbuilding KPIs like delivery speed, modular construction, or regulatory compliance.
5. Proposed Shipbuilding AI Maturity Framework
Our framework includes four stages (Beginner, Innovation, Integration, Expert) and evaluates eight dimensions: Culture, Resilience, Sustainability, Strategy, Customer Focus, Organizational Integration, Connectivity, and Production Efficiency. Each stage is validated using benchmarking data.
Table 3 summarizes the four-stage progression across the eight proposed dimensions, offering a roadmap for shipbuilding organizations to assess and advance their AI maturity in alignment with industry goals.
Table 3: AI Maturity Framework
| Dimension | Beginner | Innovation | Integration | Expert |
| Culture | Low AI literacy, resistance to change | Early experimentation with AI; supportive mindset emerging | AI embraced across teams; moderate adoption | The AI-centric culture embedded across the enterprise |
| Resilience | Reactive responses to disruptions | Basic forecasting using AI tools | Adaptive systems supported by AI for risk management | AI-driven autonomous resilience planning |
| Sustainability | Minimal awareness of green AI applications | Pilot initiatives for energy optimization | AI is used to optimize emissions and waste | Sustainability embedded as a strategic goal powered by AI |
| Strategy | No formal AI strategy | Isolated AI pilot programs aligned with select goals | AI aligned with business KPIs and strategic planning | AI drives strategic transformation across the organization |
| Customer Focus | Limited digital interaction | AI used in selected touchpoints (e.g., support bots) | Personalized services using AI analytics | Customer AI insights drive anticipatory service models |
| Organizational Integration | Siloed departments, ad-hoc AI efforts | Cross-functional AI collaboration begins | AI integrated into core business workflows | AI fully embedded in enterprise-wide processes |
| Connectivity | Low data integration, outdated systems | Partial IoT/IT-OT convergence | Real-time data pipelines and secure communications | Fully connected, interoperable, and secure digital ecosystem |
| Production Efficiency | Manual-heavy operations, low visibility | Initial automation in select operations | AI-optimized scheduling and predictive maintenance implemented | AI enhances throughput, uptime, and intelligent resource use |
Benchmarking Approach:
A hybrid benchmarking approach validated the dimensions of the proposed AI maturity model (culture, strategy, connectivity, and sustainability):
- A literature-based review compared key dimensions across 10 AI maturity models from various domains (manufacturing, government, digital transformation). Commonly recurring dimensions were retained for inclusion.
- We conducted a benchmarking analysis using data from leading shipbuilders such as China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC), Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) [27], and General Dynamics NASSCO [24], [25]. Publicly available performance data (e.g., delivery cycles, digital investment, vessel throughput, and automation level) were aligned with model dimensions to confirm relevance.
- The benchmarking highlighted that connectivity and sustainability dominate Asian shipyards (especially CSSC), while cultural alignment and strategic integration are critical for U.S. shipyards to improve. resilience. Table 4 shows the benchmarking analysis along different dimensions.
Table 4: Benchmarking Analysis
|
Dimension |
Found in Literature? | Evident in CSSC? | Evident in NASSCO? | Included in Model? |
| Culture | Yes | Partial | Partial | Yes |
| Strategy | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity | Yes | High | Limited | Yes |
| Sustainability | Moderate | High | Developing | Yes |
I am text block. Click edit button to change this text. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
6. Future Outlook and Validation Roadmap
As shipbuilding evolves under the pressure of environmental regulations and global competition, integrating AI, robotics, digital twins, and IoT-driven systems will be central to enhancing shipyard performance and sustainability. Nations such as China and South Korea are already advancing smart shipyards with high levels of automation, supported by public R&D funding and specialized technical education. For the United States to remain globally competitive, it must invest in modernizing commercial shipyards, foster public-private innovation ecosystems, and develop AI-skilled talent pipelines.
While the benchmarking approach in this study aligns AI maturity dimensions with operational benchmarks from leading shipbuilders, future validation efforts are essential to strengthen the model’s practical application. These may include:
- Field trials in selected shipyards to assess maturity progression.
- Surveys of digital adoption across U.S. and international shipyards.
- Expert panels involving maritime engineers, defense contractors, and AI strategists will refine and validate model dimensions.
- Case-based longitudinal studies to track the impact of AI adoption on delivery efficiency and sustainability metrics.
Policymakers, business executives, and shipyard operators looking to speed up digital transformation in the maritime industry will find the model’s acceptance as a strategic tool easier with the help of a well-organized validation roadmap offering empirical support.
7. Conclusion
This study proposes a sector-specific AI maturity model to guide digital transformation in shipbuilding. It bridges the gap between generic models and shipyards’ unique operational challenges. Future validation through real-world pilots and international benchmarking is recommended.
Amid fierce global competition, particularly from shipbuilding powerhouses such as China, Japan, and South Korea, these nations have secured leadership through advancements in automation, AI integration, and proactive industrial policy [7] In contrast, American shipyards face structural challenges such as higher labor and material costs, aging infrastructure, and limited automation in commercial operations [24], [25]. America must reduce reliance on foreign shipbuilders and re-establish the U.S. as a key player in the global maritime landscape. It bridges the gap between generic models and the unique operational challenges of shipyards.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
- Y.-G. Lee, C.-H. Lee, Y.-H. Jeon, and J.-H. Bae, “Transformative Impact of the EU AI Act on Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships,” Laws, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 61, Sep. 2024, doi: 10.3390/laws13050061.
- P. C. Hong, Y. S. Park, D. W. Hwang, and M. J. Sepehr, “A growth theory perspective on the competitive landscape of shipbuilding: a comparative study of Japan, Korea, and China,” Maritime Economics & Logistics, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 462–489, Sep. 2024, doi: 10.1057/s41278-023-00279-5.
- B. F. Socoliuc, A. A. Suciu, M. E. Popescu, D. A. Plesea, and F. Nicolae, “Shipyard Manpower Digital Recruitment: A Data-Driven Approach for Norwegian Stakeholders,” Economies, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 16, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.3390/economies13010016.
- “The Big Data bandwagon,” Strategic Direction, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 13–14, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.1108/SD-08-2020-0144.
- A. Cakir, Ö. Akın, H. F. Deniz, and A. Yılmaz, “Enabling real time big data solutions for manufacturing at scale,” J Big Data, vol. 9, no. 1, p. 118, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.1186/s40537-022-00672-6.
- G. Cappellesso and K. M. Thomé, “Technological innovation in food supply chains: systematic literature review,” British Food Journal, vol. ahead-of-print, no. ahead-of-print, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1108/BFJ-03-2019-0160.
- L. Jiang and S. P. Strandenes, “Assessing the cost competitiveness of China’s shipbuilding industry,” Maritime Economics & Logistics, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 480–497, Dec. 2012, doi: 10.1057/mel.2012.17.
- World Bank, “Skilled Labor Force and Industrial Transformation,” Global Competitiveness Report.
- D. Nadolny and M. Block, “Labor cost structures and competitiveness in U.S. shipbuilding,” International Journal of Maritime Engineering, vol. 165, no. A2, pp. 123–134, 2021.
- F. K, “Legacy Systems and Interoperability in Large-Scale Engineering Projects: A Case Study of U.S. Shipyards,” System Engineering, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 210–225, 2022.
- A. Martins, “Dynamic capabilities and SME performance in the COVID-19 era: the moderating effect of digitalization,” Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 188–202, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.1108/APJBA-08-2021-0370.
- E. Omol, P. Abuonji, and L. Mburu, “SMEs’ digital maturity: analyzing influencing factors and the mediating role of environmental factors,” Journal of Innovative Digital Transformation, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 19–36, Mar. 2025, doi: 10.1108/JIDT-01-2024-0002.
- M. Khraiwesh, “Measures of Organizational Training in the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI),” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 11, no. 2, 2020, doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110274.
- S. MOUHIB, H. ANOUN, M. RIDOUANI, and L. HASSOUNI, “Towards a Global Big Data Maturity Model,” in 2020 Fourth International Conference On Intelligent Computing in Data Sciences (ICDS), IEEE, Oct. 2020, pp. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICDS50568.2020.9268720.
- J. Hu and S. Gao, “Research and Application of Capability Maturity Model for Chinese Intelligent Manufacturing,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 83, pp. 794–799, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2019.05.013.
- N. B. Yams, V. Richardson, G. E. Shubina, S. Albrecht, and D. Gillblad, “Integrated AI and Innovation Management: The Beginning of a Beautiful Friendship,” Technology Innovation Management Review, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 5–18, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.22215/timreview/1399.
- W. Chen, C. Liu, F. Xing, G. Peng, and X. Yang, “Establishment of a maturity model to assess the development of industrial AI in smart manufacturing,” Journal of Enterprise Information Management, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 701–728, Mar. 2022, doi: 10.1108/JEIM-10-2020-0397.
- T. Paschou, M. Rapaccini, C. Peters, F. Adrodegari, and N. Saccani, “Developing a Maturity Model for Digital Servitization in Manufacturing Firms,” 2020, pp. 413–425. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-43616-2_44.
- “Digital Maturity Model: Achieving digital maturity to drive growth,” Deloitte.
- L. Canetta, A. Barni, and E. Montini, “Development of a Digitalization Maturity Model for the Manufacturing Sector,” in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), IEEE, Jun. 2018, pp. 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ICE.2018.8436292.
- G. Valdés, M. Solar, H. Astudillo, M. Iribarren, G. Concha, and M. Visconti, “Conception, development and implementation of an e-Government maturity model in public agencies,” Gov Inf Q, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 176–187, Apr. 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2010.04.007.
- F. Blatz, R. Bulander, and M. Dietel, “Maturity Model of Digitization for SMEs,” in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), IEEE, Jun. 2018, pp. 1–9. doi: 10.1109/ICE.2018.8436251.
- M. Kırmızı and B. Kocaoglu, “Digital transformation maturity model development framework based on design science: case studies in manufacturing industry,” Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, vol. 33, no. 7, pp. 1319–1346, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1108/JMTM-11-2021-0476.
- P. NovaKovic, “General Dynamics: Annual Report 2023,” Mar. 2024.
- J. Saballa, “General Dynamics to Build More US Navy Replenishment Ships in $6.7B Deal,” TheDeffensePost.
- S. Wang, “China State Shipbuilding Corporation’s Role in Smart Shipbuilding,” Marine Technology Reports, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 21–26, 2023.
- HD. Hyundai, “Annual Report 2023,” Hyundai Heavy Industries Group, 2024.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd., “Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Shipbuilding News,” Report.
- Dharmender Salian, Steven Brown, Raed Sbeit, "Digitalization Review for American SMEs", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 93–101, 2024. doi: 10.25046/aj090410
- Angela Pearce, "The Perceptions of Students and Teachers When using ICTs for Educational Practices Matter: A Systematic Review", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 1–12, 2022. doi: 10.25046/aj070601
- Lynne Whelan, Louise Kiernan, Kellie Morrissey, Niall Deloughry, "Towards a Framework for Organizational Transformation through Strategic Design Implementation", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 191–197, 2022. doi: 10.25046/aj070219
- Inam Abousaber, "Digital Competencies of Saudi University Graduates Towards Digital Society: The Case of The University of Tabuk", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 171–178, 2022. doi: 10.25046/aj070217
- Rachida Hassani, Younès El Bouzekri El Idrissi, "IT Project Management Models in an Era of Digital Transformation: A Study by Practice", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 53–62, 2022. doi: 10.25046/aj070205
- Valerii Dmitrienko, Serhii Leonov, Aleksandr Zakovorotniy, "New Neural Networks for the Affinity Functions of Binary Images with Binary and Bipolar Components Determining", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 91–99, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060411
- Piwai Chikasha, Kemlall Ramdass, Ndivhuwo Ndou, Rendani Maladzhi, Kgabo Mokgohloa, "Industrial Engineers of the Future – A Concept for a Profession that is Evolving", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 72–79, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060409
- Asmae Dakir, Barramou Fatima Zahra, Alami Bachir Omar, "Optical Satellite Images Services for Precision Agricultural use: A Review", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 326–331, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060337
- Kakoma Chilala Bowa, Mabvuto Mwanza, Mbuyu Sumbwanyambe, Kolay Ulgen, Jan-Harm Pretorius, "Assessment of Electricity Industries in SADC Region Energy Diversification and Sustainability", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 894–906, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj0602102
- Manuel Landum, Maria Margarida Madeira e Moura, Leonilde Reis, "A Framework for the Alignment of ICT with Green IT", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 593–601, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060268
- Irina Golitsyna, Farid Eminov, Bulat Eminov, "Teaching/Learning Strategies in Context of Education 4.0", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 472–479, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060254
- Kgabo Mokgohloa, Grace Kanakana-Katumba, Rendani Maladzhi, Sbusiso Xaba, "A Grounded Theory Approach to Digital Transformation in the Postal Sector in Southern Africa", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 313–323, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060236
- Raed Said, Anas Najdawi, Zakariya Chabani, "Analyzing the Adoption of E-payment Services in Smart Cities using Demographic Analytics: The Case of Dubai", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 113–121, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060214
- Yousra Karim, Abdelghani Cherkaoui, "Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process and Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Method Applied to Assess and Improve Human and Organizational Factors Maturity in Mining Industry", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 75–84, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060210
- Anas Najdawi, Zakariya Chabani, Raed Said, "Factors Impacting Digital Payment Adoption: An Empirical Evidence from Smart City of Dubai", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1208–1214, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj0601137
- Santo Fernandi Wijaya, Harjanto Prabowo, Ford Lumban Gaol, Meyliana, "Enterprise Resource Planning Readiness Assessment for Determining the Maturity Level of ERP Implementation in the Industry in Indonesia", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 538–549, 2021. doi: 10.25046/aj060159
- Kgabo Mokgohloa, Grace Kanakana-Katumba, Rendani Maladzhi, "Development of a Technology and Digital Transformation Adoption Framework of the Postal Industry in Southern Africa: From Critical Literature Review to a Theoretical Framework", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 1190–1206, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj0506143
- Segundo Moisés Toapanta Toapanta, Emmanuel Alejandro Narváez Picon, Luis Enrique Mafla Gallegos, "Prototype for the Management of Engineering Companies and the ICT to Improve the Quality of Services", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 698–708, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050586
- Adamu Abdullahi Garba, Maheyzah Muhamad Siraj, Siti Hajar Othman, "An Explanatory Review on Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Models", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 762–769, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050490
- Rafidah Abd Karim, Airil Haimi Mohd Adnan, Mohd Haniff Mohd Tahir, Mohd Hafiz Mat Adam, Noorzaina Idris, Izwah Ismail, "The Application of Mobile Learning Technologies at Malaysian Universities Through Mind Mapping Apps for Augmenting Writing Performance", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 510–517, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050363
- Nuno Martins, Jéssica Campos, Ricardo Simoes, "Activerest: Design of A Graphical Interface for the Remote use of Continuous and Holistic Care Providers", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 635–645, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050279
- Paolo Giammatteo, Tania Di Mascio, "Wilson-Hilferty-type Approximation for Poisson Random Variable", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 377–383, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050249
- Bayu Rahmat Setiadi, Suparmin, Slamet Priyanto, Henny Pratiwi, Sugiyono, "The Acquiring Process of Entrepreneurship Competencies in Realist Airbrush Art", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 138–142, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050218
- Airil Haimi Mohd Adnan, Mohamad Syafiq Ya Shak, Rafidah Abd Karim, Mohd Haniff Mohd Tahir, Dianna Suzieanna M Shah, "360-Degree Videos, VR Experiences and the Application of Education 4.0 Technologies in Malaysia for Exposure and Immersion", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 373–381, 2020. doi: 10.25046/aj050148
- Naima Essadi, Adil Anwar, "Coordination between Heterogeneous Models Using a Meta-model Composition Approach", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 147–157, 2019. doi: 10.25046/aj040618
- Sanae El Hassani, Hind El Hassani, Noureddine Boutammachte, "Overview on 5G Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 328–346, 2019. doi: 10.25046/aj040442
- Anatolii Petrenko, Bogdan Bulakh, "Automatic Service Orchestration for e-Health Application", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 244–250, 2019. doi: 10.25046/aj040430
- Windra Priatna Humang, Sigit Pranowo Hadiwardoyo, Nahry, "Factors Influencing the Integration of Freight Distribution Networks in the Indonesian Archipelago: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 278–286, 2019. doi: 10.25046/aj040335
- Benedikt Andrew Latos, Markus Harlacher, Florens Burgert, Verena Nitsch, Philipp Przybysz, Susanne Mütze-Niewöhner, "Complexity Drivers in Digitalized Work Systems: Implications for Cooperative Forms of Work", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 171–185, 2018. doi: 10.25046/aj030522
- Nwe Nwe, Ei Thu, "Measuring modifiability in model driven development using object oriented metrics", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 244–251, 2018. doi: 10.25046/aj030130
- Rashida Hussain, Tayyiaba Rasool, Asghar Ali, "Travelling Wave Solutions of Coupled Burger’s Equations of Time-Space Fractional Order by Novel (Gʹ/G)-Expansion Method", Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 8–13, 2017. doi: 10.25046/aj020402
