Volume 5, Issue 4

Download Complete Issue
Current Issue features key papers related to multidisciplinary domains involving complex system stemming from numerous disciplines; this is exactly how this journal differs from other interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary engineering journals. This issue contains 98 accepted papers in Network and Information system domain.
Editorial
Front Cover
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), (2020);
Editorial Board
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), (2020);
Editorial
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), (2020);
Table of Contents
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), (2020);
Articles
Offline Signature Recognition and Verification Using ORBKey Point Matching Techniques
Aravinda Chickmaglore Venkataramu, Atsumi Masahiko, Akshaya, Amar Prabhu Gurupura, Udaya Kumar Reddy Kyasambally Rajashekar
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 1-7 (2020);
View Description
An extensive work has been carried out in the field of human transcribe-verification and transcribe-recognition by extensive scholars across the globe from past decades. In order to demeanour immense experiments for considering the performance of the newly intended models and to substantiate the efficacy of the proposed model which is moderately required. This paper monologue the problem of signature-verification and recognition using diverse ORB key points and Convolution Neural Network. This method reckons on descriptors for detection and matching. The systematic approach is tested more on an few real and few fake signatures. Many features and combination of features were proposed for signature substantiation and acknowledgement. Numerous experiments are conducted to determine the capability of the proposed models in selective genuine and forgery signature. In this context, a large signature corpus comprising of 29950 offline signatures from 605 persons is created during the course of the research work. Finally the achievement was achieved about 90% of correct accuracy of the given original signature.
A Novel Representative k-NN Sampling-based Clustering Approach for an Effective Dimensionality Reduction-based Visualization of Dynamic Data
Dharamsotu Bheekya, Kanakapodi Swarupa Rani, Salman Abdul Moiz, Chillarige Raghavendra Rao
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 8-23 (2020);
View Description
Visualization plays a crucial role in the exploratory analysis of Big Data. The direct visualization of Big Data is a challenging task and difficult to analyze. Dimensionality Reduction techniques extract the features in the context of visualization. Due to the unsupervised and non-parametric nature, most of the dimensionality reduction techniques are not evaluated quantitatively and not allowed to extend for dynamic data. The proposed representative k-NN sampling-based clustering, determines the underlying structure of the data by using well-known clustering techniques. The external cluster validation index determines the order sequence of clustering techniques from which the appropriate cluster techniques are recommended for the given datasets. From the recommended set, the samples of the best clustering technique are considered as representative samples which can be used for gener- ating the visual representation. The t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) algorithm is applied to generate a low-dimensional embedding model of representative samples, which is more suitable for visualization. The new data samples are added to the generated model by using the interpolation technique. The low-dimensional embedding results are quantitatively evaluated by k-NN accuracy and trustworthiness. The performance analysis of representative k-NN sampling-based clustering results and embedding results accomplished by seven di datasets.
Citizen Behavior: The Evaluation of Complaint Application that Connected to Smart City
Evaristus Didik Madyatmadja, Hendro Nindito, Debri Pristinella
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 24-29 (2020);
View Description
SIARAN is application which is created by Government of South Tangerang City, Indonesia. The application is e-government services social media based. It is designed for citizens to be able to report problems that occur around South Tangerang City. The research was conducted to find out the factors that affect the intention of SIARAN’s users. The research model in this research was Theory of Planned Behavior which was combined by several variables of several acceptance models. The methods which were used to collect the data were literature review and questionnaire. The findings of the research were going to be developed and proceeded by using SEM-PLS (Structural Equation Model – Partial Least Square). The results of this research indicated that Information Design, Architecture, Security, Esthetical Design, give significant positive effects towards attitude. Whereas, Perceived Usefulness and Perceived Ease of Use did not give significant effects towards Attitude. Facilitating Condition and Participation Efficacy gave significant positive effect towards perceived behavior control. Perceived Behavioral Control and Attitude gave significant positive effect towards intention.
Ontologic Design of Software Engineering Knowledge Area Knowledge Components
Bulat Kubekov, Anar Utegenova, Leonid Bobrov, Vitaliy Naumenko, Aibek Ibraimkulov
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 30-34 (2020);
View Description
The article sets forth the solution of the educational resources semantic context knowledge components development task, based on the learning technology project-oriented concepts, graduate’s competency model and ontological; engineering. The being considered ontology model and knowledge display formalisms allow, firstly, relevantly image the educational resources semantic context in the support concepts ontology format, and their specifications in the form of knowledge expressions and knowledge components, and secondly, secure the knowledge components semantic interoperability withing the frame of their usage in educational environment and systems. The design process of disciplines knowledge content degree programs and individual learning guidelines is connected with specifying the knowledge content frame, the configuration of which is defined with competencies signatures and smart-contract parameters.
Adapting to Individual Differences (ATID) For Inductive Thinking and Learning Purpose
Nia Rohayati, Deni Darmawan
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 35-39 (2020);
View Description
The research in general aims to develop students’ writing skills by applying a model with reader response strategy and visual symbols to promote students’ morals. Specifically, this inquiry is expected to describe the acceptability, comparison, impact, strength, and shortcomings, and the model Adapting To Individual Differences (ATID) of Indonesian literature learning to promote writing skills. This research used a quantitative approach to a quasi-experiment design. Nevertheless, a qualitative approach was also used to analyze students’ writing. It was concluded that (1) the model of Adapting to Individual Differences (ATID) in Indonesian literature learning was able to promote students’ writing skills, (2) the model of Adapting to Individual Differences (ATID) possessed the strength comparatively in quasi-experiment class. (3) the shortcomings of the model were it spent much time as students responded both nonverbally and verbally and guided questions facilitated students to express their responses. (4) the model of Adapting to Individual Differences (ATID) indicated the significant difference to the increasing of students’ write skills in the quasi-experiment class And (5) the model of Adapting to Individual Differences (ATID) showed good qualification where the aspect of cognitive, affective, and psychomotor was developed.
A Mobile Application Design to Prevent Criminal Acts in Lima, Peru
Alexi Delgado, Enrique Lee Huamaní, Elizabeth Jenny Cortez-De La
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 40-46 (2020);
View Description
In the province of Lima, Peru, criminal acts are increasing every day; it is a social problem that affects many people, who often try with the life of the indignant person, becoming the greatest fear of the community. For this reason, a mobile application was designed that allows the inhabitants to report and share the criminal acts that occur in their environment in real time, allowing them to prevent such acts. This application was designed using the Balsamiq tool, which allows each sketch to be developed in an organized manner. The result was the development of each module that addresses each of the functionalities of the application design for its correct structuring with the Balsamiq tool. These results will help the inhabitants of Lima, Peru, to expose the facts of which they are victims, without the immediate need to go to the police station, and which will be proposed for development to different competition funds.
Energy Recovery Equipment and Control Strategies in Various Climate Regions
Rand Talib, Alexander Rodrigues, Nabil Nassif
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 47-53 (2020);
View Description
Different types of air-to-air energy recovery technologies such as coil loops, heat pipes, sensible wheels, and total energy wheels are frequently incorporated in HVAC systems in an attempt to reduce energy consumption. This study examines the impact of various types of energy recovery technologies and capacity control strategies on a building’s cooling, heating, and fan energy consumption across different climate zones, including Fargo, ND; Cincinnati, OH; Miami, FL; San Francisco, CA; and Phoenix, AZ. A self-developed analysis model simulates a typical HVAC system and compares data that will aid in evaluating different energy recovery equipment and control strategies to achieve maximum energy conservation. Conversely, the results of the study show that the improper operation and incorrect selection of energy recovery technologies could lead to increased energy consumption, further emphasizing the need for proper implementation of controls in energy recovery technologies.
Fraud Detection Call Detail Record Using Machine Learning in Telecommunications Company
Ma’shum Abdul Jabbar, Suharjito
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 63-69 (2020);
View Description
Fraud calls have a serious impact on telecommunications operator revenues. Fraud detection is very important because service providers can feel a significant loss of income. We conducted a fraud research case study on one of the operators that experienced fraud in 2009 and 2018. Call Detail Record (CDR) containing records of customer conversations such as source and destination number, call start time, duration of calls at the operator can be a source of information to use in fraud detection. The method used in this study uses machine learning with unsupervised learning techniques which are quite popular methods used in fraud detection. The purpose of this study is to propose an effective method that can be applied to detect fraud on the CDR. Variables used include caller number, number dialled, duration, fee and destination city of the dataset totalling 11,418 rows from record periods 01 to 31 May 2018. In analyzing our CDR using the K-Means and DBSCAN algorithms, we then evaluate the results to calculate accuracy by comparing to actual fraud data. Based on evaluations using confusion matrix on actual CDR fraud, we obtained the K-Means algorithm to show a better accuracy value to model fraud on telecommunications CDR compared to DBSCAN.
Robust Static Output-Feedback Fault Tolerant Control for a Class of T-S Fuzzy Systems using Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer Approach
Slim Dhahri, Essia Ben Alaia
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 70-80 (2020);
View Description
In this paper, the problems of actuator and sensor fault estimation (FE) and fault-tolerant control (FTC) for uncertain nonlinear systems represented by Takagi-Sugeno (T-S) fuzzy models are investigated. First, a robust fuzzy adaptive sliding mode observer (SMO) is designed to simultaneously estimate system states and both actuator and sensor faults. Then, using the obtained on-line FE information, a static output-feedback fault-tolerant control (SOFFTC) is developed to compensate the fault effects and stabilize the closed-loop system. Moreover, sufficient conditions for the existence of the proposed observer and controller are given in terms of linear matrix inequalities (LMIs). The robustness against uncertainties is treated using the H? optimization technique to attenuate its effect on the estimation error. Finally, the simulation results of nonlinear inverted pendulum with cart system validate the e method.
Maximum Power-Point Tracking and Stall Control with Eddy Current Brake System on Small-Scaled Wind Turbines and its Application on Agricultural Harvesting
Anupa Koswatta, Faramarz Alsharif, Yasushi Shiroma, Shiro Tamaki, Junji Tamura
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 81-93 (2020);
View Description
This research aims to enhance the generated power of the small-scaled wind turbine using the eddy current brake system and Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) control method. We analyzed the behavior of the generated power and power factor, with and without the MPPT control which implemented by eddy current brake system. Also, the feasibility of the system investigated using different wind conditions such as strong and calm wind conditions. The load data has different voltage respond to the system since its conditions depend on the day/night loads pattern, weather conditions, soil moisture. Moreover, the analogical experiment for small-scaled wind turbine blade destruction is analyzed to determine the maximum penetration value of mechanical power in order to retrieve an optimal angular velocity which resulting in provides a possible maximum power to loads. At the same time, emergency break is operated when angular velocity reaches to critical speed to avoid destruction. In the simulation, we collected the real load data from a mango farm in Okinawa prefecture in Japan. The results were analyzed through simulations for the different wind conditions. In the end of simulation, we could verify that either Maximum Power Point and emergency control are activated correspondingly.
Multi-Agent Data Recognition System Based on Received Signal in Antenna on Board Telecom System
Chafaa Hamrouni
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 94-98 (2020);
View Description
Information data recognition during traditional operating step in telecommunication system, as their interpretation, presents an important active research field. In this context, we propose as a solution multi-agent data identification system starting with received signal parameters in antenna network connected on board telecom system. Due to the Information Identification Data (IID) response variability that differ from one presented signal being to another, the IID remains difficult to detect and to recognize. In this paper, we presented a various problem related to IID recognition. We successfully developed a multimodal IID recognition based on two different modalities. We identify each hot moment relying on successful IID detected. Proposed solution is based on IID value caused by both information type and the power intensity value.
Smart Grid Users Benefits Based on DSM Algorithm Mathematical Optimization Problems Studied
Chafaa Hamrouni
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 99-104 (2020);
View Description
The purpose of this research paper is to demonstrate that optimization of energy consumption, distributed generation and storage contribute towards mutually beneficial and satisfactory Demand Side Management algorithms that can be installed into consumer smart meters or in Home Energy Storage. A new solution based on an Energy Scheduling and Distributed Storage (ESDS) and Microgrid Energy Management Distributed Optimization Algorithm Demand Side Management (MEM-DOA DSM) algorithms Microgrid Energy Management Distributed Optimization Algorithm Demand Side Management that offers benefits to consumers, utility providers, policy makers and the environment Smart grid, Demand Side Management and mathematical optimization techniques which were studied. A successful development operation of a Demand Side Management Algorithms is made by using appropriate mathematical programming methods depending on the nature of their objective functions, tests results are accomplished.
Contribution in Private Cloud Computing Development based on Study and KPI Analysis
Chafaa Hamrouni, Slim Chaoui
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 105-108 (2020);
View Description
The preset paper describes a contributes in the implementation of private Cloud Computing. Exhaustive study made validates Cloud environment creation and successful deployed Solution Configuration choice. Related solution ensures a good investment that reduces energy costs of the data center, minimizes network traffic cost proven as an NP-hard problem. In addition, each virtual machine (VsM) depends on energy within the data center. Used genetic algorithm allows the emergence of new generations, the use of Tabu search algorithm demonstrates a divergence state, however an identification technique, based on a hybrid algorithm, ensures which optimized virtual machine.
Optimization of Dual Motion Mechanism with Double Grooved Cams for High-voltage Gas Circuit Breaker
Masanao Terada, Yuki Nakai, Hiroaki Hashimoto, Daisuke Ebisawa, Hajime Urai, Yasunobu Yokomizu
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 109-118 (2020);
View Description
A novel design of a dual motion mechanism for a high-voltage gas circuit breaker is presented. The contact motion of the circuit breaker due to the operating mechanism increases capacitive current switching (CCS) performance. CCS is one of the interrupting duties of the circuit breaker, where high voltage is applied during the half cycle from contact separation. The dual motion mechanism drives two contacts in opposite directions from each other. Operating energy is reduced because the maximum displacement of the moving parts linked to the operating mechanism is shortened. To increase CCS performance at lower operating energies, the contact on the opposite side of the contact linked to the operating mechanism requires quick motion in the CCS period with a short displacement. The dual motion mechanism reported here is composed of two grooved cams that cross each other (double grooved cams). A pin positioned at the intersection point of the grooved cams rotates a lever linked to both contacts while changing the lever ratio that shortens the path length of the pin movement. To implement an optimized displacement curve with low operating energy and low mechanical stress while keeping the CCS performance high, a shape optimization method was developed that uses a direct search to minimize the local contact forces acting on the contact positions between the grooved cams and the pin. In order to maintain the stability of the pin in motion, a position holding part was designed by considering size of the gaps between the grooved cams and the pin. The measured displacement curve was in good agreement with the ideal one. In addition, a full-scale prototype was fabricated that successfully passed a 10,000-motion test.
Design of an EEG Acquisition System for Embedded Edge Computing
Kanishk Rai, Keshav Kumar Thakur, Preethi K Mane, Narayan Panigragi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 119-129 (2020);
View Description
The human brain is one of the most complex machines on the planet. Being the only method to get real-time data with high temporal resolution from the brain makes EEG a highly sought upon signal in the neurological and psychiatric domain. However, recent developments in this field have made EEG more than just a tool for medical professionals. The decreasing size and increasing complexity of EEG acquisition systems have brought it out of the lab and into the field where it is used for varied applications like neurofeedback, person recognition and other recreational activities. Amalgamation of the EEG signal with new developing standards of Industry 4.0 to control basic IOT devices using edge computing techniques marks the next step in the design and development our low-cost yet robust Brain Computer Interface (BCI); which is just one of the many applications that a versatile and well-built EEG acquisition system can be used for.
Composition of Methods to Ensure Iris Liveness and Authenticity
Ali Al-Rashid
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 130-143 (2020);
View Description
In a biometric system technology, a person is authenticated based on processing the unique features of the human biometric signs. One of the well known biometric systems is iris recognition, this technique being considered as one of the most secure authentication solutions in the biometric field. However, several attacks do exist that are able to spoof iris. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for securing the iris recognition system by eye liveness detection technique. The proposed system detects the eye liveness, and recognises the iris. This process includes multiple steps. As per the first step, the person opens his eye and the system reads remotely the changes in pupil size as a result of the response to the ambient illumination. Then, the system starts matching the iris with a database. The second step: the person closes his eye and the system remotely detects the heartbeats signals under the skin of the eyelid. As per the third step, the person opens his eyes again and the system reads the pupil size again and compares the results of the pupil size, and then the system matches again the iris with the above database. For the iris recognition to be validated, all the above checks have to be passed. We have conducted several experiments with our proposed system, based on a brand new dataset comprised of 40 subjects. In addition, we also used public terval, CASIA-Twin and Ubiris.V1. The achieved results show the quality and viability of our proposal.
A Survey on 3D Hand Skeleton and Pose Estimation by Convolutional Neural Network
Van-Hung Le, Hung-Cuong Nguyen
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 144-159 (2020);
View Description
Restoring, estimating the fully 3D hand skeleton and pose from the image data of the captured sensors/cameras applied in many applications of computer vision and robotics: human-computer interaction; gesture recognition, interactive games, Computer-Aided Design (CAD), sign languages, action recognition, etc. These are applications that flourish in Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) technologies. Previous survey studies focused on analyzing methods to solve the relational problems of hand estimation in the 2D and 3D space: Hand pose estimation, hand parsing, fingertip detection; List methods, data collection technologies, datasets of 3D hand pose estimation. In this paper, we surveyed studies in which Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) were used to estimate the 3D hand pose from data obtained from the cameras (e.g., RGB camera, depth(D) camera, RGB-D camera, stereo camera). The surveyed studies were divided based on the type of input data and publication time. The study discussed several areas of 3D hand pose estimation: (i)the number of valuable studies about 3D hand pose estimation, (ii) estimates of 3D hand pose when using 3D CNNs and 2D CNNs, (iii) challenges of the datasets collected from egocentric vision sensors, and (iv) methods used to collect and annotate datasets from egocentric vision sensors. The estimation process followed two directions: (a) using the 2D CNNs to predict 2D hand pose, and (b) using the 3D synthetic dataset (3D annotations/ ground truth) to regress 3D hand pose or using the 3D CNNs to predict the immediacy of 3D hand pose. Our survey focused on the CNN model/architecture, the datasets, the evaluation measurements, the results of 3D hand pose estimation on the available. Lastly, we also analyze some of the challenges of estimating 3D hand pose on the egocentric vision datasets.
Nearest Neighbour Search in k-dSLst Tree
Meenakshi Hooda, Sumeet Gill
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 160-166 (2020);
View Description
In the last few years of research and innovations, lots of spatial data in the form of points, lines, polygons and circles have been made available. Traditional indexing methods are not perfect to store spatial data. To search for nearest neighbour is one of the challenges in different fields like spatiotemporal data mining, computer vision, traffic management and machine learning. Many novel data structures are proposed in the past, which use spatial partitioning and recursive breakdown of hyperplane to find the nearest neighbour efficiently. In this paper, we have adopted the same strategy and proposed a nearest neighbour search algorithm for k-dSLst tree. k-dSLst tree is based on k-d tree and sorted linked list to handle spatial data with duplicate keys, which is ignored by most of the spatial indexing structures based on k-d tree. The research work in this paper shows experimentally that where the time taken by brute force nearest neighbour search increases exponentially with increase in number of records with duplicate keys and size of dataset, the proposed algorithm k-dSLstNearestNeighbourSearch based on k-dSLst tree performs far better with approximately linear increase in search time.
Modelling and Simulation of Aerodynamic Parameters of an Airship
Anoop Sasidharan Pillai, Venkata Ramana Murthy Oruganti
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 167-176 (2020);
View Description
The dynamic modelling of an airship is the primary requirement in designing and developing a control system for a particular application. Extracting/predicting/modelling the aerody- namic coefficients is a crucial step towards the modelling of an airship. There is a huge amount of literature on the aerodynamic modelling of airships which presents experimental as well as analytical methods. All these techniques require some experimental data such as the geometrical data, control derivatives, etc. In this work, we are investigating an analyti- cal technique which can calculate the aerodynamic parameters for a high altitude airship. The complete airship model is implemented using the derived aerodynamic coefficients. A MATLABOR Simulink based simulation is used for the investigation.
Industry 4.0 Operators: Core Knowledge and Skills
Olayan Alharbi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 177-183 (2020);
View Description
One of the most important technological changes due to the arrival of Industry 4.0, an initial, gradual, and complex process of technology transfer is taking place, which strongly relies on the integration of universities, industries, and governments. In this context, to make the Industry 4.0 approach a reality, several requirements need to be met. One of them is the need to qualify people to work in industries. This research paper aims to clarify the required knowledge and learning for a person to operate the manufacturing processes associated with some of the capabilities of Industry 4.0. Interviews were conducted with individuals who are Industry 4.0 employees, including experts of technology, education vendors, and employers who are eager to develop and improve their projects. This study provides several results, the most important of which is the focus on the rehabilitation of operators using modern technologies in alignment with the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Contextualization of the Augmented Reality Quality Model through Social Media Analytics
Jim Scheibmeir, Yashwant Malaiya
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 184-191 (2020);
View Description
Augmented Reality applications are gaining popularity while maintaining novelty. Many industries are utilizing the user interface type, and use cases are becoming repeat patterns of problem solutions. Despite this rising popularity, quality has not matured nor has the technology become mainstream. Novelty must be approached as risk, and risk must be evaluated for and tested to assure adequate levels of quality. Quality itself can also be vague and have contextual definition. For these reasons, a quality model for augmented reality was created. This work analyzes over two hundred thousand tweets, collected during 2019 and 2020, relating to augmented reality technology, and contextualizes various data points to the established AR Quality Model. The education industry had the highest mentions among the tweets within the scope of this research while the tweets labeled to the transportation industry had the highest sentiment. Furthermore, the tweets were shown to illustrate the needs of testing against the characteristics within the quality model; presence, perspective, interaction, portability and persistence.
Cause of Time and Cost Overruns in the Construction Project in Nepal
Bishnu Prasad Khanal, Sateesh Kumar Ojha
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 192-195 (2020);
View Description
Augmented Reality applications are gaining popularity while maintaining novelty. Many industries are utilizing the user interface type, and use cases are becoming repeat patterns of problem solutions. Despite this rising popularity, quality has not matured nor has the technology become mainstream. Novelty must be approached as risk, and risk must be evaluated for and tested to assure adequate levels of quality. Quality itself can also be vague and have contextual definition. For these reasons, a quality model for augmented reality was created. This work analyzes over two hundred thousand tweets, collected during 2019 and 2020, relating to augmented reality technology, and contextualizes various data points to the established AR Quality Model. The education industry had the highest mentions among the tweets within the scope of this research while the tweets labeled to the transportation industry had the highest sentiment. Furthermore, the tweets were shown to illustrate the needs of testing against the characteristics within the quality model; presence, perspective, interaction, portability and persistence.
High-Order Thinking Skills: The Educational Treasure Hunt Game
Yogi Udjaja, Sasmoko, Jurike V. Moniaga, Kevin Zulfian Bay
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 196-202 (2020);
View Description
Many people who have no experience want to make Games. Among them are people who only like to play Games, people who want to make business through Games, and there are also people who really want to make Games. Assume making the game is very difficult and confusing, but forget the many examples that already exist, and can evolve if modified only slightly. In this case, there are several genres of games that are quite popular, which can be changed and modified into another sub-genre. One of them is the Treasure Hunt. It is one of the well-known genres in various video games and has a straight and simple design that is also easy to understand. Which is used in a game that aims to “Find and Work”.
Entertainment Technology: Dynamic Game Production
Yogi Udjaja
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 203-206 (2020);
View Description
The times have made drastic changes in the field of technology, these changes have penetrated into various aspects, one of which is the game. Starting from the tactics of war in the real world that produces the game theory, then adopted in the form of games that exist today. Starting from without visuals to extraordinary visual elements, each of these changes always changes the way game developers in terms of making games, so that proposed methods that can adjust to the development era that can maintain quality and interest of users so that the game is made right on target, namely Dynamic Game Production.
Malware Classification Based on System Call Sequences Using Deep Learning
Rizki Jaka Maulana, Gede Putra Kusuma
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 207-216 (2020);
View Description
Malware has always been a big problem for companies, government agencies, and individuals because people still use it as a primary tool to influence networks, applications, and computer operating systems to gain unilateral benefits. Until now, malware detection with heuristic and signature-based methods are still struggling to keep up with the evolution of malware. Machine learning is known to be able to automate the work needed to detect families of existing and newly discovered malware. Unfortunately, the machine learning method using Support Vector Machine (SVM) for detecting malware can only reach a low level of accuracy. In this work, we propose a dynamic analysis method and uses a system call sequence to monitor malware behavior. It uses the word2vec technique as word embedding and implements deep learning models, namely Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Nested LSTM, as classifiers. To compare with existing machine learning approach, we also apply the Support Vector Machine (SVM) as a benchmark method. The Nested LSTM gets an accuracy of 93.11%, while the LSTM gets the best accuracy of 98.61%. The LSTM also achieved the best performance in terms of average precision at 97.57%, the average recall at 97.29%, and the average score of f1 at 97.43%. We have found that our model is lightweight but powerful for detecting malware with significant accuracy.
The Importance of Sustainability Audit Report in Go Public Companies Sector, in Indonesia
Bambang Leo Handoko, Ang Swat Lin Lindawati
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 217-222 (2020);
View Description
Sustainability is considered new for Indonesian state-owned enterprises, also has become an obligation since two years ago. More and more people are aware of the environment for the next generation, the survival of mankind in the future. Sustainability issues are no exception in Indonesia. Companies publish sustainability reports as well as financial and annual reports. This sustainability report creates a need, namely the need for audits for sustainability reports. This is often referred to as a sustainability audit or assurance report. It is a qualitative descriptive survey. Researchers collect data from the literature and study observations as well as from interviews with stakeholders. The results of our study were obtained because the increasing number of public companies reporting on sustainability requires sustainability reporting audits in Indonesian public companies. The advantage of a sustainability audit report is that, in addition to its reputation or image, it can also add value to the company’s planning, structure and accountability. Brand name of the listed company. However, there are weaknesses, the weakness lies in comparability and costs.
Dynamic Decision-Making Process in the Opportunistic Spectrum Access
Mahmoud Almasri, Ali Mansour, Christophe Moy, Ammar Assoum, Denis Lejeune, Christophe Osswald
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 223-233 (2020);
View Description
We investigate in this paper many problems related to the decision-making process in the Cognitive Radio (CR), where a Secondary User (SU) tries to maximize its opportunities by finding the most vacant channel. Recently, Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) problems attracted the attention to help a single SU, in the context of CR, makes an optimal decision using the well-known MAB algorithms, such as: Thompson Sampling, Upper Confidence Bound, e-greedy, etc. However, the big challenge for multiple SUs remains to learn collectively or separately the vacancy of channels and decrease the number of collisions among users. To solve the latter issue for multiple users, the All-Powerful Learning (APL) policy is proposed; this new policy considers the priority access and the dynamic multi-user access, where the number of SUs may change over time. Based on our APL policy, we consider as well as the Quality of Service (QoS), where SUs should estimate and then access best channels in terms of both quality and availability. The experimental results show the superiority of APL compared to existing algorithms, and it has also been shown that the SUs are able to learn channels qualities and availabilities and further enhance the QoS.
Nonlinear 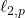 -norm based PCA for Anomaly Network Detection
-norm based PCA for Anomaly Network Detection
Amal Hadri, Khalid Chougdali, Raja Touahni
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 234-243 (2020);
View Description
Intrusion detection systems are well known for their ability to detect internal and external intrusions, it usually recognizes intrusions through learning the normal behaviour of users or the normal traffic of activities in the network. So, if any suspicious activity or behaviour is detected, it informs the users of the network. Nonetheless, intrusion detection system is usually prone to a high false positive rate & a low detection rate as a consequence of the tremendous amount of meaningless information used in the network traffic utilized to create the intrusion detection system. To overcome that, many techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA), L1-PCA and l2,p-norm based PCA were suggested. However, these methods are linear and not robust to outliers. This paper introduces the nonlinear variant of the l2,p-norm principal component analysis. Namely, the nonlinear l2,p-norm principal component analysis intends to project the data sets into a more feasible form so that the meaning of the data is damaged as less as possible. The proposed technique is not uniquely robust to outliers but keeps PCAs positive properties as well. Experimental results on the datasets KDDCup99 and NSL-KDD show that the proposed technique is extra e_ective, robust and outperform PCA, L1-PCA and l2,p-norm based PCA algorithms.
Buffering Supercapacitor Mechanism based on Bidirectional DC/DC Converter for Mini All-Terrain Vehicle Application
Syifaul Fuada, Braham Lawas Lawu, Bommegowda Kabbala Basavarajappa
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 244-251 (2020);
View Description
Fundamentally, the Bidirectional DC/DC converter consists of Buck and Boost modes, which working alternately. Hence, it has two output directions: Buck mode for decreasing the voltage and Boost mode for increasing the voltage at certain levels. In this work, we applied a non-isolated topology of the Bidirectional DC/DC converter for electric vehicle, that is mini all-terrain vehicle (ATV). We set a Buck mode to charge the Supercapacitor when the battery current and the Supercapacitor voltage are lower than considered level. Whereas the Boost mode was used to discharge as well as buffer the mini ATV when the battery current and the Supercapacitor voltage are higher than considered level. The discussion of Buck mode has been presented in previous work, so in this work, we focus on the Boost mode analysis only. This mode is set to increase the Supercapacitor’s voltage. The Supercapacitor with 25 VDC/8 Farad was used as the secondary main power inside the 22.2 VDC / 5000 mAh LiPo battery of the mini ATV motor. The mini ATV requires 36 VDC to work. Thus, it must be boosted first from 22.2 to 36 VDC using an external Boost converter. Moreover, it must be maintained at 36 VDC. Based on the requirement, we first design the bidirectional DC/DC converter involving the mathematical calculation and then simulate it into LTSpice®. The Printed-Circuit Board is then lay-outed and mounted. Later, we connected the designed system to mini ATV motor and tested the performance as well. According to the laboratory test, the Bidirectional DC/DC converter can increase (Boost) the voltage of the Supercapacitor from a certain level to 36 VDC. On the other hand, it can maintain 36 VDC. The central control in this system uses the STM32F4 Microcontroller, while the battery monitoring system employs the STMStudio.
Utilization of Data Mining to Predict Non-Performing Loan
Yosaphat Catur Widiyono, Sani Muhamad Isa
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 252-256 (2020);
View Description
In the banking industry, the existence of problem loans is inevitable. NPL (Non-Performing Loan) will certainly have an impact on the reduction in the capital of a bank. One good step in reducing the risk of credit default or the emergence of non-performing loans is to take proper care of debtors who begin to experience payment constraints. The main obstacle experienced in bank management, especially in the credit sector, is being unable to identify or detect potential debtors early due to a large amount of data and manual processing. In this study, the debtor payment history is presented as data to predict the existence of problem loans. History payment can be used to predict bad loans. The technic of data mining in this experiment is a new method. The results of research conducted using Naïve Bayes, Decision Tree, K-NN, Rule Induction, Logistic Regression, Random Forest, Generalized Linear Model, and Gradient Boosted Trees as a comparison then choose the method that has the highest accuracy to be implemented in making additional modules on the core banking system. Random Forest is the model that has the highest accuracy of 96.55%.
Diffusion of Technology for Language Challenges in the South African Healthcare Environment
Phathutshedzo Makovhololo, Tiko Iyamu
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 257-265 (2020);
View Description
Even though mobile technologies are increasingly used to enable communications between providers and receivers of healthcare services, there remain severity challenges owing to the use of various indigenous languages in many Africa countries. Some of the challenges get worst in a countries like South Africa where there are eleven official languages. As a result, interpreters and technology-enabled translation become inevitable. However, technology-enabled translation is even more complex because of the semantics that exists in the languages. The study was undertaken to identify the critical challenging factors that exists in the use of South African languages for healthcare services. The interpretivist approach was employed, and Rogers’ diffusion of innovations (DOI) theory was applied in the analysis of the data, to examine and understand how indigenous languages affects healthcare services. From the analysis, six factors were found: confidentiality, translation, interpretation, synchronisation, spoken language, and integration, and categorised into three groups, namely ethics, services and systems.
Exploring the Performance Characteristics of the Naïve Bayes Classifier in the Sentiment Analysis of an Airline’s Social Media Data
Mba Obasi Odim, Adewale Opeoluwa Ogunde, Bosede Oyenike Oguntunde, Samuel Ayodele Phillips
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 266-272 (2020);
View Description
Airline operators get much feedback from their customers which are vital for both operational and strategic planning. Social media has become one of the most popular platforms for obtaining such feedback. However, to analyze, categorize, and generate useful insight from the huge quantity of data on social media is not a trivial task. This study investigates the capability of the Naïve Bayes classifier for analyzing sentiments of airline image branding. It further examines the impact of data size on the accuracy of the classifier. We collected data about some online conversations relating to an incident where an airline’s security operatives roughly handled a passenger as a case study. It was reported that the incident resulted in a loss of about $1 billion of the company’s corporate value. Data were extracted from twitter, preprocessed and analyzed using the Naïve Bayes Classifier. The findings showed a 62.53% negative and 37.47% positive sentiments about the incident with a classification accuracy of over 0.97. To assess the impact of training size on the accuracy of the classifier, the training sets were varied into different sizes. A direct linear relationship between the training size and the classifier’s accuracy was observed. This implies that large training data sets have the potentials for increasing the classification accuracy of the classifier. However, it was also observed that a continuous increase in the classification size could lead to overfitting. Hence there is a need to develop mechanisms for determining optimum training size for finest accuracy of the classifier. The negative perceptions of customers could have a damaging effect on a brand and ultimately lead to a catastrophic loss in the organization.
Coastal Risk Modelling for Oil Spill in The Mediterranean Sea
Abdellatif Soussi, Chiara Bersani, Roberto Sacile, Dounia Bouchta, Ahmed El Amarti, Hamid Seghiouer, Driss Nachite, Jaouad Al Miys
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 273-286 (2020);
View Description
The accident probability estimation and the consequence analysis are based on statistical data about oil spill accident occurrence in the Mediterranean area, on the probability of different release sizes, and on the joint probability of wind speed and directions.
The risk model and its evaluation have been assessed for the Mediterranean littoral considering the time required by the oil slick to hit the coast in specific sensible target points assuming that an oil release accident potentially occurred in an accident sites located along the ship routes.
This approach has been applied on the area of the Strait of Gibraltar, which supports a significant volume of maritime traffic because it represents the navigational connection channel between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Optimization of the Procedures for Checking the Functionality of the Greek Railways: Data Mining and Machine Learning Approach to Predict Passenger Train Immobilization
Ilias Kalathas, Michail Papoutsidakis, Chistos Drosos
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 287-295 (2020);
View Description
Information is the driving force of businesses because it can ensure the ability of knowledge and prediction. The railway industry produces a huge volume of data, with the proper processing of them and the use of innovative technology, there is the possibility of beneficial information to be provided which constitute the deciding factor for the correct decision making. Safety is the railway comparative advantage that has to be reinforced by each business administration while making the optimum decisions. The main purpose of this paper is the investigation of the most important dysfunctions that arise in a train and can cause its immobilization at the main passenger rail, resulting in huge delays of conducting the routes setting the passengers at risk. Afterwards the total of malfunctions is assessed and the most important, potentially, malfunction is assessed, so as the executives of the Greek Railway company to plan and redefine the processes and the initial plan of the predictive maintenance. This paper demonstrates the effort of implementing innovative applications by making use of methods from the rapidly developed field of Data Mining to the Greek Railway Company that uses obsolete procedures for the control of the trains’ functionality in order to investigate the data for the provision of specialized information which will be used as a tool for the faster, more accurate and precise decision making. This decision making approach is based on a specific algorithm’s design in order to automatically detect faults and make periodic maintenance of trains easier. Holistic approach is performed in the management of real data from the Greek railway industry and a predictive model of Machine Learning is developed, for the optimization of the management’s performance of the trains reinforcing the strategic target of the railway industry which is the transportation of citizens with safety and comfort.
Cluster Centroid-Based Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for WSN-Assisted IoT
Nalluri Prophess Raj Kumar, Josemin Bala Gnanadhas
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 296-313 (2020);
View Description
Wireless sensor network is highly resource constrained, where energy efficiency and network lifetime plays a major role for its sustenance. As the sensor nodes are battery operated and deployed in hostile environments, either recharging or replacement of batteries in sensor nodes is not possible after its deployment in inaccessible areas. In such condition, energy is the vital factor for the survival of sensor node in the sensing field. In order to increase the network lifetime and balance the energy consumption, robust routing protocols are required. The proposed network routing has three phases: 1. Network initiation phase to create a zone which enables the communication among local nodes 2. Zone co-ordinator selection phase algorithm to form zone cluster and its re-election procedure and 3. Zone head selection with its replacement phase based on energy centroid positional information and distance to the basestation to distribute load equally among zone co-ordinators, local sensor nodes. The data path between zone heads and basestation is distance centric and is optimized at one hop and dual hop levels to avoid data packet loss at zoneheads. Each zone is designed to own atmost ¼ rth of deployed sensor node count through uniform random deployment. Simulations results when basestation is placed inside sensing field indicates that the proposed network algorithm outperforms when benchmarked against similar protocols like conventional LEACH, Traditional PEGASIS, existing PRRP, ES3 protocols in terms of performance metrics like Network energy consumption, Average energy consumed by sensor node, Packet delivery ratio, Packet loss percentage and Network throughput.
Deep Learning Model for A Driver Assistance System to Increase Visibility on A Foggy Road
Samir Allach, Mohamed Ben Ahmed, Anouar Abdelhakim Boudhir
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 314-322 (2020);
View Description
For many years, a lot of researches have been made to develop Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) that are based on integrated systems. The main objective is to help drivers. Hence, keeping them safe under different driving conditions. Visibility for drivers remains the biggest problem faced on the road in an atmosphere of fog. In this paper, we examine a system that can be employed to substantially enhance visibility through using deep neural networks. Researches done recently- which are based on deep learning for eliminating image fog- have made clear that an end-to-end proposed system is such an effective model. However, it becomes a must to extend the idea to end-to-end real-time video deshazing. In this paper, we introduce a model of image dehazing. It is based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) as a basis for developing the video dehazing model. As in addition, we concatenate our model with the faster RCNN for detecting objects on the road in real time.
The experimental results on our image datasets shows the performance of our model with regard to Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR=19.823) and Structural Similarity (SSIM =0.8501). On the dataset of the synthesized videos, our model achieved a performance of PSNR = 21.4032 and SSIM = 0.9354. Moreover, with the concatenation of our dehazing model with Faster R-CNN (regions with convolutional neural networks), our proposed system displays desirable visual quality and a remarkable progress of the object detection achievement on blurred images with mean Average Precision (mAP) equal to 0.933 during the day and 0.804 during the night.
Logistics Solutions in the Preparation Phase for the Appearance of Disasters
Erika Barojas-Payán, Diana Sánchez-Partida, Miguel-Josué Heredia-Roldan, Victorino Juárez-Rivera, Jesús Medina-Cervantes
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 323-330 (2020);
View Description
Natural disasters have caused not only economic but also human losses. These events bring with them, among other things, deficiencies in the supply of food, clothing, health and cleaning products, to name a few. This situation makes it imperative to locate facilities that can supply the needs, as mentioned earlier, to the victims in the shortest possible time. This document presents the evaluation of a logistic model of the literature whose foundations are: a) the classic p-median problem for the location of a pre-positioning warehouse; b) an extension of the (q-R) model for calculating inventories of different products, according to different types of demand, and c) the problem of multiple vehicles routing with the capacity to establish delivery routes from warehouses to the affected municipalities. This model is evaluated with 90 municipalities belonging to Veracruz, Mex. The results show that the location of the warehouse falls in the municipality of Fortín de las Flores, the inventory levels for five demands and four product kits, and product delivery routes, which are a total of 12, with which a favorable cost minimization is obtained.
Distributed Microphone Arrays, Emerging Speech and Audio Signal Processing Platforms: A Review
Shahab Pasha, Jan Lundgren, Christian Ritz, Yuexian Zou
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 331-343 (2020);
View Description
Given ubiquitous digital devices with recording capability, distributed microphone arrays are emerging recording tools for hands-free communications and spontaneous tele-conferencings. However, the analysis of signals recorded with diverse sampling rates, time delays, and qualities by distributed microphone arrays is not straightforward and entails important considerations. The crucial challenges include the unknown/changeable geometry of distributed arrays, asynchronous recording, sampling rate mismatch, and gain inconsistency. Researchers have recently proposed solutions to these problems for applications such as source localization and dereverberation, though there is less literature on real-time practical issues. This article reviews recent research on distributed signal processing techniques and applications. New applications benefitting from the wide coverage of distributed microphones are reviewed and their limitations are discussed. This survey does not cover partially or fully connected wireless acoustic sensor networks.
Computational Intelligence and Statistical Learning Performances on Predicting Dengue Incidence using Remote Sensing Data
Nittaya Kerdprasop, Kittisak Kerdprasop, Paradee Chuaybamroong
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 344-350 (2020);
View Description
Dengue is a viral infection disease transmitted to people through the bite of specific mosquito species living in a tropical zone. According to the World Health Organization, dengue has been listed among the top-ten diseases for 2019 as it makes 3.9 billion people in 128 countries be at risk of infection. One major cause of substantial dengue widespread is the globally warm climate that accelerates rapid growth of mosquito vectors. In this research, we aim to build data-driven models to predict dengue cases using satellite index data to represent temperature, humidity, and greenness over the surface area of Bangkok, which is our target area of dengue prediction because of its high infection cases. Oceanic Niño Index is also used as a predictor variable to represent climate variability. The modeling methods employ seven algorithms from two broad schemes of the machine learning field. Artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) are algorithms from the subfield of computational intelligence, whereas multiple linear regression (MLR), generalized linear model (GLM), support vector regression (SVR), classification and regression tree (CART), and chi-squared automatic interaction detection (CHAID) are from the statistical learning subfield. Performances of these algorithms are evaluated on the same set of out-of-sample data. The results are that ANFIS is the best model for predicting dengue outbreak in the capital city of Thailand.
Design and Optimization of a Three Stage Electromechanical Power Unit using Numerical Methods
Yashwant Kolluru, Rolando Doelling, Lars Hedrich
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 351-362 (2020);
View Description
The advent of electric vehicles has changed the face of the automobile industry. The drive system properties of vehicles such as eBikes or electric cars differ fundamentally from those of a diesel engine. The lack of a conventional internal combustion engine has made the vehicles considerably silent. Nevertheless, previously hidden sources of vibration and noise have become more dominant. In addition to these emissions, other structural properties such as compliance and deformation also appear as relevant factors for the original equipment manufacturer. Usually, deterioration of these variables affects the efficiency of the power unit. In this paper, a simulation template is created to understand and analyze these properties of the drive unit. Furthermore, new enhancements to improve the key indicators, such as strain energy, natural frequencies, etc., are shown, thereby creating a potential method flow to develop better performing drive units. Numerical optimization tools are used to simulate structures with complex shapes that exactly meet the mechanical constraints and use as little material as possible. In this work, two optimized variants of electromechanical drives are presented. The first scenario illustrates the optimized model with an objective of minimizing the strain energy of the structures, whereas the second task aids in the development of a variant with superior dynamic properties than the current drive units. Ultimately, several numerical calculations are validated using experiments.
Bilateral Communication Device for Deaf-Mute and Normal People
Raven Carlos Tabiongan
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 363-373 (2020);
View Description
Communication is a bilateral process and being understood by the person you are talking to is a must. Without the ability to talk nor hear, a person would endure such handicap. Given that hearing and speech are missing, many have ventured to open new communication methods for them through sign language. This bilateral communication device can be utilized by both non-sign language users and Deaf-mute together in a single system. Shaped as a box (8in x 8in) with two multi-touch capable displays on both ends, the contraption has several microcontrollers and touch boards within. The latter has the technology of twelve interactive capacity touch and proximity electrode pads that react when tapped, producing quick response phrases audible via speaker or earphone. These touch boards are equipped with an MP3 decoder, MIDI synthesizer, 3.5mm audio jack and a 128MB microSD card. The touch screen modules mounted on top of the microcontrollers transfer data to and from each other in real-time via receiver-transmitter (RX-TX) full duplex UART serial communication protocol. The device is lightweight weighing at about 3 lbs. The prototype device was piloted in an academic institution of special education for deaf-mute students. Participants were 75 normal and 75 Deaf-mute people aged between 18 and 30 years. The experimental results show the overall rating of the device is 90.6%. The device is designed to promote the face-to-face socialization aspect of the Deaf-mute users to the normal users and vice versa. Several third-party applications were utilized to validate the accuracy and reliability of the device thru metrics of consistency, timing and delay, data transmission, touch response, and screen refresh rates.
Survey Analysis: Enhancing the Security of Vectorization by Using word2vec and CryptDB
Hana Yousuf, Said Salloum
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 374-380 (2020);
View Description
Vectorization is extracting data from strings through Natural Language Processing by using different approaches; one of the best approaches used in vectorization is word2vec. To make the vectorized data secure, we must apply a security method, which will be CryptDB. The paper is analyzing the survey, which is created to interview security engineers through the SPSS tool. By analyzing the responses from software security engineers, it is seen that both word2vec and CryptDB works significantly. Word2vec is an effective vectorization approach, while CryptDB is an effective, secure database. In future work, we will be developing a secure vectorization using both approaches
Development of Soil Moisture Monitoring by using IoT and UAV-SC for Smart Farming Application
Sarun Duangsuwan, Chakree Teekapakvisit, Myo Myint Maw
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 381-387 (2020);
View Description
Soil moisture is a fundamental factor for smart farming that is used to control the water management system. In this paper, the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) small cell (UAV-SC) can provide Internet of things (IoT) as the hotspot mobility network, due to the minimum limitation energy of connected IoT. The development of ground sensor (GS) communicates to the UAV-SC called GS-UAV-SC model for soil moisture monitoring is proposed to smart farming. UAV-SC aims to fulfill the data collection task with a limitation of GSs power. In the experiment, the two case scenarios: Napier grass farm and Ruzi grass farm are implemented. The result of soil moisture status is demonstrated as an example of data in real time on a mobile application monitoring system. The proposed system is useful for users/farmers to know the soil moisture data quickly for smart farming applications.
The Role of KM in Enhancing AI Algorithms and Systems
Hani AlGhanem, Mohammad Shanaa, Said Salloum, Khaled Shaalan
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 388-396 (2020);
View Description
Knowledge Management processes present a vital role in improving AI systems and algorithms. Many studies and reviews were carried out to examine the relationship between KM processes and AI systems. However, studies were focusing on specific methods and the impact on some AI algorithms, neglecting the role of other KM processes and how it may affect the AI system to achieve the objective, which reduces the adoption in some organizations. The current study shows the relation between KM processes and AI systems from a higher perspective, giving different options to apply other KM processes for the same AI algorithm to reduce any implementation challenges and enhance the adoption level. The review looks into 16 studies collected from a different database from 2014 to 2019. The main finding of the research was the massive impact of some KM processes like knowledge acquisition and knowledge creation on the different types of AI systems and algorithms to give an additional option for organizations during the implementation. Additionally, the research finds that most of the studies agree on the positive relationship between knowledge management processes and the role-plays to enhance AI systems and algorithms. Finally, the study shows a decrease in the number of researches done for this topic in the selected databases, which can be enhanced by other researchers by examining other databases to increase results accuracy.
Potential of Solar Energy in Residential Rooftop Surface Area in Semarang City, Indonesia
Djoko Adi Widodo, Purwanto Purwanto, Hermawan Hermawan
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 397-404 (2020);
View Description
This study examines the potential of solar energy in the urban environment with a case study in Semarang, Indonesia by analyzing the intensity of solar radiation and the residential rooftop area. The study aims to obtain a quantitative description of the potential for electricity production from rooftop solar photovoltaic systems in residential areas and estimate the mitigation potential of CO2 . The estimation method has adopted the hierarchies assessment: estimation of physical, geographic, and technical potential. This study shows the residential roof area spread over 16 districts in the city of Semarang is 412,987.50 m2 to 2,083,387 m2 has the average potential to of solar energy every year of 44,051 – 222,222 MWh/year. Total the low-carbon electricity is equivalent to 40.87% of the total electricity consumption in 2018 at Semarang City and reduce 1,394 tonCO2 in a year. Potential electricity production is proposed to set rules for the future empowerment of solar energy and analyze the potential at different time levels, such as monthly, weekly and daily.
Keyword Driven Image Description Generation System
Sreela Sreekumaran Pillai Remadevi Amma, Sumam Mary Idicula
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 405-411 (2020);
View Description
Image description generation is an important area in Computer Vision and Natural Language Processing. This paper introduces a novel architecture for an image description generation system using keywords. The proposed architecture uses a high-level feature such as keywords for generating captions. The important component of caption generation is the deep Bidirectional LSTM network. The space and computational complexity of the system are smaller than that of the CNN feature-based image description generation system. The number of parameters is also small in the keyword-based image description generation system. It generates novel meaningful sentences for images. The systems performance depends on the keyword extraction system.
Tidal Propagation Based On Co-Phase Chart and Co-Range Chart in Sunda Strait, Indonesia
Denny Nugroho Sugianto, Harjo Susmoro, Khoirol Imam Fatoni, Virginia Stephanie Claudia, Haris Djoko Nugroho
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 412-418 (2020);
View Description
The characteristic of tide is different for each region. Co-tidal charts are one of the media to present an information about the character of tidal. There are two types of co-tidal chart, such as co-phase chart and co-range chart. Co-phase chart will show the distribution of tides, meanwhile the co-range chart will show the propagation direction of tides. Sunda Strait was chosen to analyze the tidal propagation pattern. The amount of the tidal station which were observed are 33 stations across Sunda Strait. This research used four harmonic constituents of tide, such as M2, S2, K1 O1 and the chart of Sunda Strait to establish co-tidal charts. The harmonic constituent of tide was analyzed by Admiralty Method. These data were obtained from Hydrography and Oceanography Center, Indonesian Navy (PUSHIDROSAL). The result of this research shows the tidal propagation direction of semidiurnal harmonic constituents of tide (M2, S2) that flows in south area of Sunda Strait (comes from Indian Ocean through the western part of Sumatra island). Meanwhile, in north area of Sunda Strait, the tidal propagation that comes from Indian Ocean flows through Karimata Strait. The direction of tidal propagation of diurnal harmonic constituents of tide (K1, SO1) that flows in Sunda Strait comes from Pacific Ocean through Karimata Strait. However, the tidal type in Sunda Strait is dominated by mixed tide prevalling semidiurnal and the highest amount of Z0 is 100 cm, meanwhile the lowest value of Z0 in Sunda Strait is 40 cm.
Fuzzy-logical Control Models of Nonlinear Dynamic Objects
Siddikov Isamiddin Xakimovich, Umurzakova Dilnoza Maxamadjonovna
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 419-423 (2020);
View Description
The article considers the task of developing a fuzzy-logical PID-type controller for a nonlinear dynamic system. A feature of the structure is presented, which consists in simplifying its controller by decomposition. In the simplest version, three fuzzy controllers are used with one input and one output and separate rule bases. Parameters of fuzzy controllers are optimized using a genetic algorithm. A two-step controller tuning scheme for a nonlinear dynamic object is proposed. At the first step, the genetic algorithm is used to tune the linear PID controller; it is shown that the obtained coefficients are used at the output of each channel of the fuzzy PID controller. At the second step, using a genetic algorithm, a nonlinear transforming function is formed for each channel, implemented on the basis of an artificial neural network. The control algorithm is debugged and tested using the MatLab system. The results show a significant improvement in the characteristics of the transient process compared to traditional controllers.
A Framework of E-Procurement Technology for Sustainable Procurement in ISO 14001 Certified Firms in Malaysia
Pratik Kumar Singh, Fadillah Binti Ismail, Chan Shiau Wei, Muhammad Imran, Syed Ashfaq Ahmed
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 424-431 (2020);
View Description
With the current emerging development pattern in Malaysia, E-Government has been unveiled by the Malaysian Government to be one of the multimedia super corridor flagship applications to implement digital technology to improve government operations. E-procurement was originally utilized by businesses to minimize turnaround times and prices, but recently it was often used as a platform for sustainable procurement. However, there have been few attempts to investigate E-procurement technology in Malaysia concerning sustainable procurement. Also, there is no consistent and reliable framework of E-procurement technology for sustainable procurement practices. The focal area of this research is ISO 14001 accredited firms in Malaysia, the population of these organizations is 55, sample size (N)=162 respondents including procurement managers, executives and staff which are involved directly or indirectly in the process of procuring products and services. This study is conceptual and aims to explore how the adoption of E-procurement technologies influence sustainable procurement practices within ISO 14001 accredited firms in Malaysia.
Effects of Oversampling SMOTE in the Classification of Hypertensive Dataset
Nurhafifah Matondang, Nico Surantha
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 432-437 (2020);
View Description
Hypertensive or high blood pressure is a medical condition that can be driven by several factors. These factors or variables are needed to build a classification model of the hypertension dataset. In the construction of classification models, class imbalance problems are often found due to oversampling. This research aims to obtain the best classification model by implementing the Support Vector Machine (SVM) method to get the optimal level of accuracy. The dataset consists of 8 features and a label with two classes: hypertensive and non-hypertensive. Overall test result performance is then compared to assess between SVM combined with SMOTE and not. The results show that SMOTE can improve the accuracy of the model for unbalanced data into 98% accuracy compared to 91% accuracy without SMOTE.
A CNN-based Differential Image Processing Approach for Rainfall Classification
Roberta Avanzato, Francesco Beritelli
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 438-444 (2020);
View Description
With the aim of preventing hydro-geological risks and overcoming the problems of current rain gauges, this paper proposes a low-complexity and cost-effective video rain gauge. In particular, in this paper the authors propose a new approach to rainfall classification based on image processing and video matching process employing convolutional neural networks (CNN). The system consists of a plastic shaker, a video camera and a low cost, low power signal processing unit. The use of differential images allows for greater robustness, guaranteeing full background subtraction. As regards precision, speed and ability to adapt to variations in precipitation intensity, the proposed method achieves good performance. In particular, the results obtained from seven classes, ranging from “No rain” to “Cloudburst”, applying the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) to the differential images on 16×16 sub-blocks show an average accuracy of 75% considering, also, the adjacent miss-classification. Furthermore, the analysis of precision and sensitivity parameters yields excellent results.
The proposed method is very innovative, in fact, the few studies found in the state of the art use only two classification classes (No rain and Rain), while our method contains seven classification classes and overall delivers very good accuracy performance.
Artificial Intelligence Approach for Target Classification: A State of The Art
Maroua Abdellaoui, Dounia Daghouj, Mohammed Fattah, Younes Balboul, Said Mazer, Moulhime El Bekkali
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 445-456 (2020);
View Description
The classification of static or mobile objects, from a signal or an image containing information as to their structure or their form, constitutes a constant concern of specialists in the electronic field. The remarkable progress made in past years, particularly in the development of neural networks and artificial intelligence systems, has further accentuated this trend. The fields of application and potential uses of Artificial Intelligence are increasingly diverse: understanding of natural language, visual recognition, robotics, autonomous system, Machine learning, etc.
This paper is a state of the art on the classification of radar signals. It focuses on the contribution of artificial intelligence to the latter without forgetting target tracking. This by evoking the different feature extractors, classifiers and the existing identification deep learning algorithms. We detail also the process allowing carrying out this classification.
Assessing the Operator’s Readiness to Perform Tasks of Controlling by the Unmanned Aerial Platforms
Dmytro Kucherov, Olha Sushchenko, Andrii Kozub, Volodymyr Nakonechnyi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 457-462 (2020);
View Description
Together with the intensity of development in the field of technology of unmanned platforms and their effective use for solving various tasks of peacetime and war, the requirements for the training of the operator managing the platform also increase. This fully applies to personnel providing the flight of manned means. Nevertheless, there are significant differences in the requirement of operator preparedness for an unmanned platform. This is, first of all, control in conditions of remoteness from an unmanned platform, orientation on the display of the control panel, delays in the passage of information, and possibly a complete loss of communication. In such conditions, the requirements for the reaction time of the operator increase, he must also have the ability to anticipate the development of the situation, be able to work with available equipment for a long time. These and several other criteria determine the general criterion of operator productivity, which is introduced in the work. The productivity criterion is a linear convolution function of particular criteria with some weighting factors, the exact values of which are unknown. A detailed analysis of particular criteria made it possible to establish their inconsistency and heterogeneity. The article proposes an approach that allows us to eliminate the inconsistency of local criteria by separately calculating weight coefficients for each part based on the hierarchy analysis method. The basic properties of the proposed approach are also given; modeling confirms the correctness of the solutions. This approach can be useful in the certification of operators of various fields of activity.
Short-Term Dynamic Exchange Rate Model: IFEER Concept Development
Anton Kuzmin
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 463-468 (2020);
View Description
The new model of the short-term exchange rate dynamics was constructed. First of all, the most interesting were the reasons of the deviation from the medium-term equilibrium. The author’s IFEER-concept (International Flows Equilibrium Exchange Rate) was used as a base and it was developed. In this study, due to the short-term modeling period the differential approach was applied. The result was an integrated version of the exchange rate dynamics model. The main result of mathematical modeling is a nonlinear multi-factor functional dependence of the exchange rate. The result dynamic functional dependence differs from the previous medium-term dependencies by the type of the internal dynamic function. Economically, this function in the short-term period is responsible for explosive changes in the exchange rate dynamics. The basis for mathematical modeling was the system of fundamental economic factors that affect the dynamics of the exchange rate. The influence of crisis events on the Russian financial market in the short term was studied. The conducted research allowed us to analyze and evaluate the quantitative impact of the short-term effects of the dynamics of the exchange rate of the Russian ruble to the US dollar.
The Sound of Trust: Towards Modelling Computational Trust using Voice-only Cues at Zero-Acquaintance
Deborah Ooi Yee Hui, Syaheerah Lebai Lutfi, Syibrah Naim, Zahid Akhtar, Ahmad Sufril Azlan Mohamed, Kamran Siddique
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 469-476 (2020);
View Description
Trust is essential in many interdependent human relationships. Trustworthiness is measured via the effectiveness of the relationships involving human perception. The decision to trust others is often made quickly (even at zero acquaintance). Previous research has shown the significance of voice in perceived trustworthiness. However, the listeners’ characteristics were not considered. A system has yet to be produced that can quantitatively predict the degree of trustworthiness in a voice. This research aims to investigate the relationship between trustworthiness and different vocal features while considering the listener’s physical characteristics, towards modelling a computational trust model. This study attempts to predict the degree of trustworthiness in voice by using an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model. A set of 30 audio clips of white males were obtained, acoustically analyzed and then distributed to a large group of untrained Malaysian respondents who rated their degree of trust in the speakers of each audio clip on a scale of 0 to 10. The ANOVA test showed a statistically significant difference of trust ratings across different types and intensities of emotion, duration of audio clip, average fundamental frequencies, speech rates, articulation rates, average loudness, ethnicity of listener and ages of listener (p <.01). The findings conclude that Malaysians tend to trust white males who talk faster and longer, speak louder, have an f0 between 132.03Hz & 149.52Hz, and show a neutral emotion or rather stoic (arousal<.325). Results suggest that Indians are the most trusting Malaysian ethnic group, followed by Bumiputera from East Malaysia and then followed by Malays. Chinese are the least trusting Malaysian ethnic group. The data was fed into an ANN model to be evaluated, which yielded a perfect percentage accuracy (100%) in degree of trustworthiness 39.70% of the time. Given a threshold of two-point deviation, the ANN had a prediction accuracy of 76.86%.
Study Of The Effect Of Abnormalities In The External Ear Inducing Hearing Problems
Jihane Melloui, Jamila Bakkoury, Omar Bouattane
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 477-487 (2020);
View Description
Tinnitus is a phenomenon for which the patient hears sound in the absence of any external sound source. To this day, there is no cure for this phantom sound perception. But it can be masked temporarily to help relief the patient’s pain. In order to allow this, a better understanding of the phenomenon is needed. A validated acoustic model of the outer ear developed by the authors is used in this study. This model allows to study the effect of the presence of an anomaly (a cavity, a swelling or a foreign fluid) in the human auditory canal. These anomalies are modeled as a modification of the section of the ear canal or as an alternation of the medium of sound propagation in the ear canal. A parametric study involving the position, width and height of the anomaly as well as the sound velocity in the ear canal is conducted. The results obtained make it possible to conclude on the effect of each parameter on the frequency response of an auditory canal with anomaly.
Neural Network-Based Fault Diagnosis of Joints in High Voltage Electrical Lines
Marco Bindi, Igor Aizenberg, Riccardo Belardi, Francesco Grasso, Antonio Luchetta, Stefano Manetti, Maria Cristina Piccirilli
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 488-498 (2020);
View Description
In this paper a classification system based on a complex-valued neural network is used to evaluate the health state of joints in high voltage overhead transmission lines. The aim of this method is to prevent breakages on the joints through the frequency response measurements obtained at the initial point of the network. The specific advantage of this kind of measure is to be non-intrusive and therefore safer than other approaches, also considering the high voltage nature of the lines. A feedforward multi-layer neural network with multi-valued neurons is used to achieve the goal. The results obtained for power lines characterized by three and four junction regions show that the system is able to identify the health state of each joint, with an accuracy level greater than 90%.
Remote Control of Garden Plantation Water Pumps using Arduino and GSM Mobile
Beza Negash Getu, Mohamed Abdulkadir, Michael Tous
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 499-504 (2020);
View Description
A remotely mobile phone controlled electronic system for supplying water to garden plantations in a greenhouse or similar environment was designed and experimentally implemented. The system monitors the garden environmental conditions such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity and sunlight and a remote user can send commands from his mobile phone such as to switch ON/OFF water pumps, supply water for the plants for certain duration and acquire the environmental status information of the plantation. The water pumps are controlled by the Arduino microcontroller that is the core part of the electronic system. The user has the ability to monitor the environmental conditions on his mobile phone. Such systems can facilitate monitoring, give flexibility of controlling, save time and human labour and increase productivity as a result of automation and remote controlling.
Decision Making System for Improving Firewall Rule Anomaly Based on Evidence and Behavior
Suchart Khummanee, Phatthanaphong Chomphuwiset, Potchara Pruksasri
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 505-515 (2020);
View Description
Firewalls are controlled by rules which often incur anomalies. The anomalies are considered serious problems that administrators do not desire to happen over their firewalls because they cause more vulnerabilities and decrease the overall performance of the firewall. Resolving anomaly rules that have already occurred on the firewall is difficult and mainly depends on the firewall administrator’s discretion. In this paper, a model is designed and developed to assist administrators to make effective decisions for optimizing anomaly rules using the probability approach (Bayesian). In this model, the firewall needs to add four property fields (Extra fields) to the firewall rules: frequency of packets matching against rules, evidence of creating rules, the expertise of rules creator and protocol priority. These fields are used to calculate the probability of each firewall rule. The probability for each rule is used while the rules conflict and administrators need to resolve them. The rule having the highest probability value indicates that it has the highest priority in consideration. Experimental results show that the proposed model allows firewall administrators to make significant decisions about solving anomaly rules. The data structure of this model is based on k-ary tree, therefore the speed of building tree, time complexity and space complexity: O(n), O(logmn) and O(m*n) respectively. Besides, the confidence of the proposed firewall for resolving firewall rule anomalies of the administrator increase by 29.6% against the traditional firewall, and the reliability value between the inter-raters also increase by 13.1%.
IoT Based Human Activity Recognition System Using Smart Sensors
Deepti Sehrawat, Nasib Singh Gill
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 516-522 (2020);
View Description
Internet of Things provides a virtual view of real-life things by guiding challenges faced by persons in daily life. It is reforming our world with trillions of sensors and other IoT enabled devices by creating a smart environment. Effective use of IoT sensors in various smart IoT applications is very important. After analyzing different sensor applications, this paper presents various types of wearable sensors used for monitoring of human activities along with different locations optimal for their placement. This paper enlightens sensors suitable for any particular application. IoT has opened up a new avenue of research in the field of human activity recognition using wearable sensors. It provides an individual’s valuable information regarding functional ability and lifestyle. Human activities are monitored automatically to provide personalized support to different individuals. Recently, various researchers presented different human activity recognition systems, a few are cumulated in this paper. Furthermore, a Human Activity Recognition (HAR) system is also proposed in this paper for a smart IoT environment that would be secure enough to use.
Damage Accumulation Model for Cracked Pipes Subjected to Water Hammer
Zakaria Mighouar, Laidi Zahiri, Hamza Khatib, Khalifa Mansouri
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 523-530 (2020);
View Description
During service, oil and gas pipelines may be exposed to cyclical loads during service, which may lead to a structural failure. Failure is due in most cases to cracks in the structure. Mechanics of the propagation of surface cracks pose a serious challenge and, therefore, models are required to help analyze it. In this study, a nonlinear model is proposed to estimate the accumulation of fatigue damage in the case of defected pipes subjected to a water hammer. The studied pipes are in the presence of a semi-elliptical longitudinal surface crack. This numerical model allows the load sequence to be considered when the structure is under variable amplitude loading. The validated model is used in a parametric analysis, the purpose of which is to determine the influence of the fluid transported and the defect parameters on the evolution of the accumulated damage. The results allow the conclusion of the parameters that have the most impact on the harmfulness of the crack defect as well as the most dangerous cracks in the case of a pipe subjected to water hammer.
Development of an Adaptive HVAC Fuzzy Logic Controller for Commercial Facilities: A Case Study
Hamidi Meryem, Bouattane Omar, Raihani Abdelhadi, Khalili Tajeddine
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 531-539 (2020);
View Description
This paper is a case study of the integration of an energy management system (EMS) in a commercial building. A detailed analysis of this EMS’s impact on energy consumption is presented. High energy demand is very common in commercial and industrial facilities. With this in mind, the present work aims to improve the energy consumption rate within a commercial facility by proposing an energy management system based on a central fuzzy logic controller. Thus, the central controller adapts the energy management to a pre-established schedule taking at consideration primarily the Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) of the targeted building.
Human-Robot Multilingual Verbal Communication – The Ontological knowledge and Learning-based Models
Mohammed Qbadou, Intissar Salhi, Hanaâ El fazazi, Khalifa Mansouri, Michail Manios, Vassilis Kaburlasos
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 540-547 (2020);
View Description
In their verbal interactions, humans are often afforded with language barriers and communication problems and disabilities. This problem is even more serious in the fields of education and health care for children with special needs. The use of robotic agents, notably humanoids integrated within human groups, is a very important option to face these limitations. Many scientific research projects attempt to provide solutions to these communication problems by integrating intelligent robotic agents with natural language communication abilities. These agents will thus be able to help children suffering from verbal communication disorders, more particularly in the fields of education and medicine. In addition, the introduction of robotic agents into the child’s environment creates stimulating effects for more verbal interaction. Such stimulation may improve their ability to interact with pairs. In this paper, we propose a new approach for the human-robot multilingual verbal interaction based on hybridization of recent and performant approach on translation machine system consisting of neural network model reinforced by a large distributed domain-ontology knowledge database. We have constructed this ontology by crawling a large number of educational web sites providing multi-lingual parallel texts and speeches. Furthermore, we present the design of augmented LSTM neural Network models and their implementation to permit, in learning context, communication between robots and children using multiple natural languages. The model of a general ontology for multilingual verbal communication is produced to describe a set of linguistic and semantic entities, their properties and relationships. This model is used as an ontological knowledge base representing the verbal communication of robots with children.
Development Trends of Smart Cities in the Future – Potential Security Risks and Responsive Solutions
Vu Nguyen Hoa Hong, Luong Tuan Anh
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 548-556 (2020);
View Description
Smart cities are an indispensable development of the ongoing urbanization process world- wide. Currently, smart cities are being built and deployed by countries in the first steps. Based on research on the current state of developing smart cities in the world, the author forecasts the future development trends of such cities, pointing to one of the major challenges for cities. It is a problem that responds to potential security risks. Identifying potential risks for coping solutions is essential for the future of smart sustainable cities. Main solutions include policy and law solutions, technology solutions and raising the peoples standard were given in the article.
Application of EARLYBREAK for Line Segment Hausdorff Distance for Face Recognition
Chau Dang-Nguyen, Tuan Do-Hong
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 557-566 (2020);
View Description
The Hausdorff distance (HD) is defined as MAX-MIN distance between two geometric objects for measuring the dissimilarity between two objects. Because MAX-MIN distance is sensitive with the outliers, in face recognition field, average Hausdorff distance is used for measuring the dissimilarity between two sets of features. The computational complexity of HD, and also average HD, is high. Various methods have been proposed in recent decades for reducing the computational complexity of HD computing. However, these methods could not be used for reducing the computational complexity of average HD. Line Hausdorff distance (LHD) is a face recognition method, which uses weighted average HD for measuring the distance between two line edge maps of face images. In this paper, the Least Trimmed Square Line Hausdorff Distance method, LTS-LHD, is proposed for face recognition. The LTS-LHD, which is a modification of the weighted average HD, is used for measuring the distance between two line edge maps. The state – of – art algorithm, the EARLYBREAK method, is used for reducing the computational complexity of the LTS-LHD. The experimental results show that the accuracy of proposed method and LHD method are equivalent while the runtime of proposed method is 68% lower than LHD method.
Organizational Agility Assessment of a Moroccan Healthcare Organization in Times of COVID-19
Fadoua Tamtam, Amina Tourabi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 567-576 (2020);
View Description
Since its appearance, COVID-19 has severely impacted the healthcare sector all over the world. The healthcare organizations should be agile in order to cope with this new health crisis. Indeed, organization agility was highly recommended as an essential basis for flexibility, innovation, speed, as well competitiveness. Different research provided different conceptual models suitable to evaluate the organization agility. In this sense, this paper presents an assessment model, which by defining different agile enablers, criteria and attributes, aims at identifying the least and the most suitable enablers influencing the healthcare organization agility. To realize it practically, this paper uses the fuzzy logic approach which provides the improvement directions for enhancing the organization agility. Subsequently, the data gathered from a Moroccan healthcare organization was substituted in this assessment model and the level and the suggestions improvement for agility were derived. In this way, the organization will integrate the successful combination of the agility enablers in this dynamic environment.
A Support Vector Machine Based Technique for Fault Detection in A Power Distribution Integrated System with Renewable Energy Distributed Generation
Katleho Moloi, Yskandar Hamam, Jacobus Andries Jordaan
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 577-588 (2020);
View Description
The integration of renewable energy distributed generation (REDG) into the energized distribution power grid has become more popular in recent years. This has been escalated by the general global energy shortages. The REDG has proven to be effective for energy sustainability and reliability. However, there are technical challenges which arise from integrating REDG into the energized power grid. These challenges include the effectiveness of power grid protection against faults. In this paper, a fault diagnostic algorithm is proposed to detect faults in a power system integrated with REDGs. The algorithm utilizes wavelet packet transform (WPT) for signal filtering, support vector machine (SVM) for fault classification and detection. The proposed algorithm is validated using the Eskom 90 bus electrical system and the results obtained show that faults can be detected with a high accuracy of 99%. The Eskom 90 bus system is modelled using DigSilent platform and the algorithm is tested on the WEKA software.
Overview of Solar Radiation Estimation Techniques with Development of Solar Radiation Model Using Artificial Neural Network
Amar Choudhary, Deependra Pandey, Saurabh Bhardwaj
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 589-593 (2020);
View Description
Estimation Solar radiation is the most significant part of the optimization of solar power. This may be achieved if the solar radiation is predicted well in advance. Meteorological stations have radiation measuring devices like pyranometer, pyrheliometer, radiometer, solarimeter, etc. however, it may not be available at the location of interest for researchers. Due to this limitation solar radiation estimation models are devised based on location details like Altitude, Latitude, Longitude, and metrological details like Wind Speed, Ambient Temperature, Relative Humidity, Day Temperature, etc. These radiation models provide Global Solar Radiation (GSR) as output. These models are statistically tested based on error calculation like Mean Bias Error, Mean Absolute Error, Root Mean Square Error, etc. This paper is framed to briefly provide the idea behind different solar radiation estimation models with the methodology used. Soft computing-based models are mainly analyzed here. ANN-based Global Solar Irradiance Estimation Model has been developed using geographical parameters like Elevation, Latitude, Longitude, Longitude, and meteorological parameters like Months of a year, Days of a month, Temperature, Atmospheric Pressure, Relative Humidity, and Wind Speed. The data are downloaded from the National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB) for 2014 (latest available). From this paper, the reader will come to know about various techniques used in solar radiation estimation. The developed ANN-based model has better results for training, testing, validation, and all with Regression value of 0.94304, 0.9488, 0.94766, 0.94556 respectively. The MSE is found to be 0.0089147 at epoch 0. The obtained values of R and MSE indicates the suitability of the developed model.
Customer Satisfaction Recognition Based on Facial Expression and Machine Learning Techniques
Moulay Smail Bouzakraoui, Abdelalim Sadiq, Abdessamad Youssfi Alaoui
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 594-599 (2020);
View Description
Nowadays, Customer satisfaction is important for businesses and organizations. Manual methods exist, namely surveys and distributing questionnaires to customers. However, marketers and businesses are looking for quick ways to get effective and efficient feedback results for their potential customers. In this paper, we propose a new method for facial emotion detection to recognize customer’s satisfaction using machine-learning techniques. We used a facial landmark point; we extract geometric features from customer’s emotional faces using distances from landmarks points. Indeed, we used distances between the neutral side and the negative or positive feedback. After that, we classified these distances by using different classifier, namely Support Vector Machine (SVM), KNN, Random Forest, Adaboost, and Decision Tree. To assess our method, we verified our algorithm by using JAFFE datasets. The proposed method reveals 98,66% as accuracy for the most performance SVM classifier.
Real-Time Traffic Sign Detection and Recognition System for Assistive Driving
Adonis Santos, Patricia Angela Abu, Carlos Oppus, Rosula Reyes
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 600-611 (2020);
View Description
Road traffic accidents are primarily caused by drivers error. Safer roads infrastructure and facilities like traffic signs and signals are built to aid drivers on the road. But several factors affect the awareness of drivers to traffic signs including visual complexity, environmental condition, and poor drivers education. This led to the development of different ADAs like TSDR that enhances vehicle system. More complex algorithms are implemented for improvement but this affects the performance of a real-time system. This study implements a real-time traffic sign detection and recognition system with voice alert using Python. It aims to establish the proper trade-off between accuracy and speed in the design of the system. Four pre-processing and object detection methods in different color spaces are evaluated for efficient, accurate, and fast segmentation of the region of interest. In the recognition phase, ten classification algorithms are implemented and evaluated to determine which will provide the best performance in both accuracy and processing speed for traffic sign recognition. This study has determined that Shadow and Highlight Invariant Method for the pre-processing and color segmentation stage provided the best trade-off between detection success rate (77.05%) and processing speed (31.2ms). Convolutional Neural Network for the recognition stage not only provided the best trade-off between classification accuracy (92.97%) and processing speed (7.81ms) but also has the best performance even with lesser number of training data. Embedded system implementation utilized Nvidia Jetson Nano with interface Waveshare IMX219-77 camera, Nvidia 7” LCD and generic speaker and programmed in Python with OpenCV, sci-kit learn and Pytorch libraries. It is capable of running at an adaptive frame rate from 8-12 frames per second with no detection and down to approximately 1 frame per second when there is a traffic sign detected.
Performance Analysis of Go-Back-N ARQ Protocol Used In Data Transmission Over Noisy Channels
Fayza Ahmed Nada
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 612-617 (2020);
View Description
Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) protocols are used to control transmission errors in data communications. They are used at Data Link Control (DLC) sublayer of Data Link Layer (DLL) of OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) network model to achieve flow and error control and provide smooth and reliable transmission between network nodes. ARQ protocols use acknowledgments and timeouts to satisfy reliable data transmission over noisy channels. Types of ARQ protocols include Stop-and-wait ARQ, Go-Back-N ARQ, and Selective Repeat ARQ. This paper presents a new mathematical model to analyze performance of Go-Back-N ARQ protocol over noisy channels. Many performance measures of Go-Back-N ARQ protocols are discussed. The analysis uses Stochastic Process and a two-dimensional Markov Chain to present the proposed model. We study the distributions of system occupancy and waiting time when implementing Go-Back-N ARQ protocol in data transmission. Results include: Probability Generating Functions (PGF) of system occupancy and waiting time. Moreover, mean values of previous system parameters are derived. ARQ protocols are essential for peer-to-peer protocols that provide reliable data transmission. The obtained results can be adopted and implemented in simulations of similar communication systems or approximating relevant systems.
Modeling and Transformation from Temporal Object Relational Database into Mongodb: Rules
Soumiya Ain El Hayat, Mohamed Bahaj
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 618-625 (2020);
View Description
With such a big volume of data growing tremendously every day, and the storage of important volume of data becoming increasingly more flexible, NoSQL(Not only SQL or Non-Relational ) database are designed to store a large amount of information and are growing for big data systems in web analytics. It an approach does not require any specific schema and avoid the use of the joins to store or retrieve the information. To ensure the availability and scalability many industries are now replacing their object relational database in many systems by adopting NoSQL database technology for e-business applications. It is document-oriented databases which help in grouping data more logically. This paper describes a disciplined approach of migration and proposes a model transformation from temporal Object relational database (TORDB) Into Mongo db. Also, this paper approach deals with a novel data integration methodology in order to manipulate and the store the varying time data in Json (Java Script Object Notation) documents.
Modelling and Simulation of 3-DOF Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot using Force Feed Forward Control
Pham Van Bach Ngoc, Le Thi Hong Gam, Dam Hai Quan, Bui Trung Thanh, Nguyen Luong Thien
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 626-632 (2020);
View Description
This research the authors design the intelligent control for 3-DOFs lower limb rehabilitation robot base on the complex dynamics equation. The Force Feed-Forward Method (FFM) is promote to control the of 3-DOFs lower limb rehabilitation robot including dynamics characteristics. The robot can sense the force of the therapist which exerted on the robot and patient’s leg, then produces necessary forces through joints at the hip, knee, and ankle. The force feedforward controller is used to compensate the force generated by the therapist to perform patient-active exercises. In this paper, firstly authors briefly introduce 3-DOFs lower limb rehabilitation robot, next the kinematics and dynamics equation of 3-DOFs lower limb rehabilitation robot established base on Lagrange-Euler method are presented, and then the control method is introduced. Last, the performance of the proposed control methods has been confirmed by numerical simulations of the robot in all three joints: hip, knee, and ankle.
Earthquake Response of Multi-Storey Infilled Reinforced Concrete Buildings
Miloud Mouzzoun, Abdelkader Cherrabi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 633-637 (2020);
View Description
The aim of this work is to study the effect of infill brick panels on the response of multi-storey buildings under seismic loading. An eight storey building is investigated. The building is analysed under gravity and seismic loads. Infill panel is replaced by two struts according to FEMA306. Time history and pushover analyses are performed to assess seismic strength of the building. Simulations are performed by SAP2000. Numerical results show that behavior of bare and infill frames under lateral loading are too distinct. There is a change in the manner in which the infill frame carries the lateral loads.
Machine Learning for Network Intrusion Detection Based on SVM Binary Classification Model
Anouar Bachar, Noureddine El Makhfi, Omar EL Bannay
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 638-644 (2020);
View Description
Recently, the number of connected machines around the worldwide has become very large, generating a huge amount of data either to be stored or to be communicated. Data protection is a concern for all institutions, it is difficult to manage the masses of data that are susceptible to multiple threats. In this work, we present a novel method of Intrusion Detection System (IDS) based on the detection of anomalies in computer networks. The aim is to use artificial intelligence techniques in the form of Machine Learning (ML) for intrusion detection. For this purpose, we have proposed a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification model with two kernels, one Polynomial and the other Gaussian. This model is trained and tested with the recent UNSWNB-15 dataset. Regarding the results obtained, we have evaluated our model with six metrics capable of offering all potential threats. As a result, we have achieved a percentage of 94% for the detection rate (DR).
COVID-19 Crises: Global Economic Shocks vs Pakistan Economic Shocks
Naveeda K. Katper, Muhammad Nawaz Tunio, Niaz Hussain, Attaullah Junejo, Faheem Gul Gilal
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 645-654 (2020);
View Description
This paper documents, information about the current outbreak of Corona virus and its multidimensional effects witnessed worldwide. The objective of the study is to disseminate information to policymakers, government and the general public, to facilitate the efforts for fighting against the contagious virus and aims to contribute to the economic and social welfare. Though the data changes rapidly by every passing minute, yet the current scenario may be analyzed to evaluate the present situation for a fruitful outcome. Hence, the discussion may be useful for all the stakeholders (government, policymakers and the public) for their reference. Various studies previously observed that widespread contagious diseases have a severe impact on the economy. It is observed that the faster and wider the outbreak of disease, the higher and severer the influence on the economies. The economies face shrinkage of income, revenue, earnings, while health expenditure increases for hospitals, medical kits, ventilators, uniforms, masks, gloves, medicines and other medical equipment. Therefore, it has a two-pronged adversely hitting effect on economies to manage the imbalance in the budget and fiscal matters. Another unfortunate situation is when the high populated country is poor too. The world has realized the effects of the different contagious viruses in the different times in history. Nevertheless, the virulence and the severity of the COVID-19 is far greater than the previous viral breakouts. We, in this research attempt to highlight the multidimensional effects of COVID-19 and create some possibilities how to deal and fight with this cruel and invisible enemy.
Social-Interactive Learning Concept Used for Electronic Educational Resource “Post-Graduate Foreign Language” and the Obtained Learning Curve
Natalya Chernova, Victor Chernov, Margarita Emelianova, Raisa Akhunzianova, Danil Sukhopluev
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 655-659 (2020);
View Description
The article touches upon an urgent question of social-interactive learning. The resource under study deals with one of the possible ways to solve this problem, in the context of global socio-cultural transformations and a new paradigm for the development of society. It is the formation of a subject-subject dialogue between a teacher and a student. The second language research study showed how pre-and intermediate speakers’ performance breaks down in the face of a difficult narrative task and self-regulation and control over the mediational means are lost. More advanced speakers are able to guide themselves through the task. The main idea of such education is that good learning leads to development. It seems to us important to refer the concept of the zone of proximal development to the development of the individual, which affects the boundaries of the zone of proximal development. Electronic educational resource with the help of mediating means or sign operations makes external social interactions become “internalized”, namely, internally reconstructed psychological processes – ways of thinking and learning A student identifies active personality development prospect through the actual experience. The students’ learning curve let us prove the idea that IT technologies intensify the process of studying, but should provide not only language accomplishments but active communication with a teacher as well.
Correlation-Based Incremental Learning Network for Gas Sensors Drift Compensation Classification
Panida Lorwongtrakool, Phayung Meesad
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 660-666 (2020);
View Description
A gas sensor array is used for gas analysis to aid in an inspection. The signals from the sensor array are fed into machine learning models for learning and classification. These signals are characterized by time series fluctuating according to the environment or drift. When an unseen pattern is entered, the classification may be incorrect, resulting in decreased model performance. Creating a new model results in the problem of forgetting the old knowledge called Catastrophic Forgetting. Accordingly, this research proposes Correlation-Based Incremental Learning Network (CILN) using the Correlation Distance method to measure similarity and the Gaussian membership function to determine membership of each node. The gas sensor array data is used to verify the proposed algorithm by choosing 16 steady-state features (DR) from 13,910 records which are divided into 6 classes: 1) Ethanol, 2) Ethylene, 3) Ammonia, 4) Acetaldehyde, 5) Acetone, and 6) Toluene. The data are normalized and divided as the training sets into 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, and 50%, respectively. The proposed algorithm was compared with well-known classifiers. CILN experiment results yield the highest accuracy of 98.96% using 50% of the training data set. It shows that CILN has the incremental learning ability and can be used with data that fluctuate according to the situation.
Design of a Flapping Wings Butterfly Robot based on Aerodynamics Force
Kanjanapan Sukvichai, Kan Yajai
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 667-675 (2020);
View Description
Insect robots are always amazed by humans due to their ability to fly using a wing flapping mechanism. The butterfly robot was designed in this research based on aerodynamics and aeroelastic especially for designing a flapping mechanism due to its complexity. A butterfly wing structure was designed by considering aerodynamics forces based on assumptions. Aerodynamic equations were derived in order to obtain lift and thrust forces that acted on a small wing section. The wing was assumed to be in the Quasi-steady state when it was analyzed based on the thin airfoil theorem. Airflow was simulated in order to obtain air pressure and vertexes acting on the wing surface when it swings in the still air. By integrating the wing section’s lift force for a flapping cycle motion trajectory, the average lift force was obtained. The robot wing structure was designed based on the average lift. The real butterfly wing was used as the guideline for designing the robot wing. Each wing was fabricated from a laminar plastic sheet. Carbon fiber robs were used as an internal reinforced support structures for wing frames. The reinforced wing achieved the wing’s rigidity and was considered as a thin airfoil. The flapping mechanism was designed by using two separated servo motors because of its flexibility and performance. This mechanism enables the robot’s rotation without an extra actuator. The butterfly robot body was manufactured from the 3D printer using PLA material. The experiments were conducted to identify the robot performance. The designed butterfly robot can take off from the support platform and fly up to a certain height.
Clustering of Mindset towards Self-Regulated Learning of Undergraduate Students at the University of Phayao
Pratya Nuankaew
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 676-685 (2020);
View Description
The effects of Covid-19 severely affected the Thai higher education model. Therefore, there are three significant objectives in this research: (1) to cluster the mindsets and attitudes toward self-regulated learning styles of undergraduate students at the University of Phayao. (2) to construct a predictive model for recommending an appropriate student learning clusters. (3) to evaluate the predictive model that has been constructed. Samples collected a compilation of 472 student satisfaction with questionnaires from three schools, with seven disciplines at the University of Phayao, Thailand. Research tools consisted of statistical and machine learning techniques as follows: frequency, percentage, average, standard deviation, k-means clustering, decision tree techniques, cross-validation methods, confusion matrix performance, accuracy, precision, and recall measurement. Researcher found that the k-means model with the highest accuracy is the decision tree model that was classified into three clusters by dividing the model testing into the leave-one-out cross-validation method with a depth of seven levels of the decision tree model and an accuracy of 98.73%. From the results and studies, it can be concluded that the developed model is effective and reasonable to be further developed as an application for further organizational development.
Fuzzy Recognition by Logic-Predicate Network
Tatiana Kosovskaya
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 686-699 (2020);
View Description
The paper presents a description and justification of the correctness of fuzzy recognition by a logic-predicate network. Such a network is designed to recognize complex structured objects that can be described by predicate formulas. The NP-hardness of such an object recognition requires to separate the learning process, leaving it exponentially hard, and the recognition process itself. The learning process consists in extraction of groups of features (properties of elements of an object and the relations between these elements) that are common for objects of the same class. The main result of a paper is a reconstruction of a logic-predicate recognition cell. Such a reconstruction allows to recognize objects with descriptions not isomorphic to that from a training set and to calculate a degree of coincidence between the recognized object features and the features inherent to objects from the extracted group.
Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Topic Classification in an Online Submission System
Tran Thanh Dien, Nguyen Thanh-Hai, Nguyen Thai-Nghe
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 700-709 (2020);
View Description
Topic classification is a crucial task where knowledge categories exist within hierarchical information systems designed to facilitate knowledge search and discovery. An application of topic classification is article (e.g., journal/conference paper) classification which is very useful for online submission systems. In fact, numerous online journals/magazine submission systems usually receive thousands of article submissions or even more for each month. This leads to a huge amount of time-consumption of editors to process and categorize the submissions aiming to look for and assign appropriate reviewers to the submitted articles. In this study, we propose an approach based on natural language processing techniques and machine learning algorithms (both classic machine learning and deep learning) to automatic classify the topics of articles in an online submission system. We show by promising performance collected from prediction tasks to present that the proposed method is a potential approach for applying to the real system.
Bathtub-Shape Failure Rate Life Time Model in a New Version with the use of Bayesian Prediction Bounds for the Presence of Outliers
Ayed Rheal A. Alanzi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 710-714 (2020);
View Description
The present article explains obtaining of the Bayesian prediction bounds at the maximum and minimum rate taking into account the results of future observation from a new version of a bathtub-shape failure rate distribution of life time type in the presence of outliers. The Type-II censored sample serves as a basis for the intervals of the prediction with the numerical examples as illustrations of the studied procedure.
Interpolatory Projection Techniques for H2 Optimal Structure-Preserving Model Order Reduction of Second-Order Systems
Md. Motlubar Rahman, Mohammad Monir Uddin, Laek Sazzad Andallah, Mahtab Uddin
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 715-723 (2020);
View Description
This paper focuses on exploring efficient ways to find H2 optimal Structure-Preserving Model Order Reduction (SPMOR) of the second-order systems via interpolatory projection-based method Iterative Rational Krylov Algorithm (IRKA). To get the reduced models of the second- order systems, the classical IRKA deals with the equivalent first-order converted forms and estimates the first-order reduced models. The drawbacks of that of the technique are failure of structure preservation and abolishing the properties of the original models, which are the key factors for some of the physical applications. To surpass those issues, we introduce IRKA based techniques that enable us to approximate the second-order systems through the reduced models implicitly without forming the first-order forms. On the other hand, there are very challenging tasks to the Model Order Reduction (MOR) of the large-scale second-order systems with the optimal H2 error norm and attain the rapid rate of convergence. For the convenient computations, we discuss competent techniques to determine the optimal H2 error norms efficiently for the second-order systems. The applicability and efficiency of the proposed techniques are validated by applying them to some large-scale systems extracted form engineering applications. The computations are done numerically using MATLAB simulation and the achieved results are discussed in both tabular and graphical approaches.
Towards Classification of Shrimp Diseases Using Transferred Convolutional Neural Networks
Nghia Duong-Trung, Luyl-Da Quach, Chi-Ngon Nguyen
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 724-732 (2020);
View Description
Vietnam is one of the top 5 largest shrimp exporters globally, and Mekong delta of Vietnam contributes more than 80% of total national production. Along with intensive farming and growing shrimp farming area, diseases are a severe threat to productivity and sustainable development. Timely response to emerging shrimp diseases is critical. Early detection and treatment practices could help mitigate disease outbreaks, leading to on-site diagnostics, instant services recommendation, and front-line treatments. The authors establish a con- tribution hub for data collection in the ethnographic fieldwork of Mekong delta. Several deep convolutional neural networks are trained by applying the transfer learning technique. We have investigated six common reported shrimp diseases. The classification accuracy is achieved of 90.02%, which is very useful in extremely non-standard images. Throughout the work, we raise the attention of shrimp experts, computer scientists, treatment agencies, and policymakers to develop preventive strategies against shrimp diseases.
Determination of ERP Readiness Assessment Using Agile Parameters: A Case Study
Santo Fernandi Wijaya, Harjanto Prabowo, Ford Lumban Gaol, Meyliana
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 733-740 (2020);
View Description
At present, in the era of digitization the organizations need Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to have the ability adapt to changes with rapid response in order to increase the competitive advantage. The fact, many companies have failed to implement ERP which is proven to be not go live on time, so that the implementation value is to be very expensive. For this reason, it is important to consider other methods that can reduce failures in implementing ERP that are reviewed from the perspective of readiness assessment. Based on previous research, there are some challenging on the ERP readiness assessment. We also found that some areas on the ERP readiness that still not explore more serious such as ERP and agile method. Therefore, based on the challenging and open are on the ERP readiness, we will explore more development the framework of ERP readiness assessment using agile parameters to help the industry. The purpose of this research is to identify gaps and propose improvements which are the weaknesses in order to improve performance of the organization. The result of this research is developing the framework using an agile parameter for determination of the ERP readiness assessment with a case study in the textile industry in Indonesia. Hopefully, this research has contribution as a measurement tool for assessing the organizational readiness in order to increase agility in the industry. This research methodology uses the combination of qualitative and quantitative research methods using the NVivo software as a result of FGD data processing and using the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity (TOPSIS) for validation and verification tests.
A Review on Cross-Layer Design Approach in WSN by Different Techniques
Sultana Parween, Syed Zeeshan Hussain
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 741-754 (2020);
View Description
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) include a large number of sensor nodes that are connected to each other with the limitations in energy sources, battery life, memory, mobility and computational capacity. Since the traditional layered architecture was appropriate only for the wired network. It works within a strict boundary that leads to more energy usage as well as more communication traffic. It also impacts on the overall network lifespan and performance of the system. Energy efficiency and network lifespan are the primary concern of WSN due to the fact that each node in the network operates with extremely limited energy. Recent studies have shown that the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model cannot meet the demands of the wireless sensor network.
To overcome such limitations, the cross-layer design has been introduced. It allows direct interactions between protocol at non-adjacent layers. In this paper, we present different types of cross-layer design techniques in Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) and discusses several cross-layer proposals given by researchers. At the end, the paper highlights some challenges faced in implementing CLD in Wireless Sensor Networks.
Design and Implementation of a PLC Trainer Workstation
Matthew Oluwole Arowolo, Adefemi Adeyemi Adekunle, Martins Oluwaseun Opeyemi
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 755-761 (2020);
View Description
The Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an important component for industrial automatic engineering operation. Hence, the need to comprehend its basis of operation becomes an inevitable task. Some of the problems is industrial PLC is an expensive, pre-built hardware kit, acquisition of programming software and its requisite programming competence is a challenge. Thus, this paper present’s the design steps for a desktop PLC trainer workstation for industrial automatic engineering operation. Although researchers have proposed and reported several PLC trainers but they fail to discuss the hardware connection of the input/output components neither is the basic PLC automatic – operation nor PLC component symbols with description discussed. These are the areas discussed in this paper to train participant on PLC programming knowledge. The develop PLC workstation consist of push buttons and switches for input signals and for output signal buzzer, indicator lights and blower. The control aspect comprises the PLC, timer and relay. The PLC module is the MITSUBISHI FX 1S-30MR-001, the simulation software is the MITSUBISHI FXTRN-BEG-EL and the programming software is the MITSUBISHI GX Developer version 8. Authors presented two automatic control application scenarios to train participants and evaluate how the trainer is applicable to real-world situation. We conducted a survey after training to measure the impact of our approach for PLC programming knowledge for participants and result show enhanced knowledge in design step module and LL programming module significantly with our approach.
An Explanatory Review on Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Models
Adamu Abdullahi Garba, Maheyzah Muhamad Siraj, Siti Hajar Othman
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 762-769 (2020);
View Description
Cybersecurity is growing exponentially day by day in both the public and private sectors. This growth also comes with a new and dynamic cyber-threats risk that causes both sectors’ performance to halt. These sectors must update their cybersecurity measures and must understand the capability and maturity of their organization’s cybersecurity preparedness. Cybersecurity maturity models are widely used to measure how ready an organization is when it comes to cybersecurity. The main aim of this article is to conduct a comprehensive review of the current cybersecurity capability maturity models using a systematic review of published articles from 2011 to 2019. A comparative study was conducted based on Hal- vorsen and Conradi’s taxonomy. The review indicated almost all the cybersecurity maturity model consists of similar elements like maturity levels and processes but significantly lacks the validation process, it was observed each of the models were predominantly designed for a specific purpose and also for different organization size and application domain.
A Method for Detecting Human Presence and Movement Using Impulse Radar
Young-Jin Park, Hui-Sup Cho
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 770-775 (2020);
View Description
Using non-invasive and non-contact sensors to measure a person’s presence or movement helps improve the quality of life for both healthy people and patients. In this paper, a method of measuring the presence and motion of a person is proposed by utilizing UWB Impulse Radar, which is low power consumption and safe to radiate to the human body. The experimental stage of this study is divided into the stage of extracting features by signal processing from radar signals, the stage of generating datasets with 3~6 kinds of labels, and the stage of performing and verifying machine learning by imaging. In this experiment, a small number of images were used because only good quality signals were selected and used by radiating radar signals to the human body. The experiment result show high accuracy when using neural networks such as GoogLeNet and SqueezeNet. Experiments in this study confirmed that radar signals could be used to detect human presence and motion as a result of studies using the proposed method.
Ethics as a Motivation Indicator in Second Language Vocational Digital Teaching
Natalya Viktorovna Matveeva, Ludmila Vladimirovna Makar
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 776-782 (2020);
View Description
The non-selective second language course at vocational colleges and universities makes teachers strive at fostering students’ motivation to learn by choosing from a variety of enhancing factors. Teacher’s personality and skills if they comply with pedagogical ethics are considered to be inspiring for students to learn. The aim of this piloting study was to collect empirical data and ascertain the actual motivational power of ethical teaching skills when organizing and conducting autonomous learning activities for college students on the example of educational computer games.
The ethical teaching skills applied when creating and using computer games as out-of-classroom voluntary activities were conceptualized. Their possible influence on learning motivation of college students was analysed with the use of oral and written feedback procedures, and statistical data retrieved from Metrika.Yandex and students’ certificates submitted.
This allowed to determine five specific groups of students valuing the activity, which in their turn were united into two larger formations: students with distinct intrinsic motivation in the activities-related areas (60%) and socially and psychologically responsive students (40%). A possible method to evaluate statistically the efficiency of some ethical skills specified is suggested, whereas the other skills need further research under modified parameters.
Thus, ethical teaching skills are effective in the case the college students possess an intrinsic motivation in an area actualized by an activity suggested. Therefore, they are unlikely to be regarded as an independent motivator, but the indicator of a particular intrinsic motivation characteristic to a student.
The Effects of Transmission Power and Modulation Schemes on the Performance of WBANs in on-Body Medical Applications
Marwa Boumaiz, Mohammed El Ghazi, Mohammed Fattah, Anas Bouayad, Moulhime El Bekkali
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 783-794 (2020);
View Description
Wireless Body Area Networks support the operation within multiple frequency bands. Thus, they can be integrated in several applications, one of which is on-body medical monitoring applications, as concerned in this paper. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to present the impact of transmission power and both of Differential Binary Phase Shift Keying and Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying modulation schemes, on the performance of a WBAN model based on the IEEE 802.15.6 2.4 GHz narrow-band, dedicated to on-body medical applications. This involves identifying the modulation scheme(s) and transmission power level(s) to be adopted for these applications, that can be classified into three types depending on their data rate (low, medium and high data rate medical applications), in order to meet Packet Loss Rate and latency requirements. The numerical study has confirmed that the adoption of DBPSK modulation and low transmission powers provides good performance for low data rate monitoring applications. At medium data rates, a relatively increased transmit power was required. However, at high data rates, DQPSK modulation with a 0 dBm transmission power seemed to be the right choice to be made in terms of the mentioned performance indicators.
Non-Ridership Presumption Toward New Bus Rapid Transit Purwokerto-Purbalingga Executio
Fauzan Romadlon
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 795-804 (2020);
View Description
Bus Rapid Transit in Purwokerto-Purbalingga is a new mass transportation mode. Recently, the execution of the BRT has been going on for three years. In terms of service standards to ridership, the BRT has been fulfilled the requirement. However, during the execution, it shall be supported by the non-ridership (local communities) who get the impact as public engagement. The non-ridership impact is captured by observing their presumptions. This study uses quantitative method and survey technique to collect the data by spreading questionnaires to the non-ridership in Purwokerto and Purbalingga. The collected data is analyzed by Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and Structural Equation Modelling Partial Least Square (SEM-PLS). The ANOVA results show that gender, age ratio, and residence (living area) are significant presumption factors. According to SEM-PLS model, the R-squared of non-ridership presumption variables toward the BRT execution as excellent public transportation is at 51.8% (moderate level). It is found that the economic variable affects the excellent public transportation variable is at 41.4%, and the social variable have a correlation with the excellent public transportation variable is at 36.2%, but not with the environment variable (5.6% only). Following up these findings, it is recommended that public engagement through the non-ridership presumption will lead the BRT provider to purpose some programs to improve the service and increase the occupancy. So that, the proposed program will attract the sense of awareness and public engagement of the non-ridership toward the BRT execution.
Mentoring Model in an Active Learning Culture for Undergraduate Projects
Wongpanya Nuankaew, Kanakarn Phanniphong, Sittichai Bussaman, Direk Teeraputon, Pratya Nuankaew
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 805-815 (2020);
View Description
Senior projects allow students to move the learning process from basic knowledge to an interdisciplinary approach. The purpose of this research is (1) to analysis attitude and perception, which is a collaboration between teachers and students to develop a model for clustering of appropriate advisors and advisee who cooperate in senior project, and (2) to develop factors that are significant to predict the right match in senior projects course. Data collection was a questionnaire consisting of 463 samples from 7 administrators, 68 lecturers, 26 staff and 362 students from two institutions: The Rajabhat Mahasarakham University, and the University of Phayao. The research methodology was designed and divided into three sections: preparation, implementation, and conclusion. The result shows that the satisfaction and the overall acceptance level were at a high level (mean = 4.04, S.D. = 0.88). Moreover, the developed model has the highest level of efficiency (accuracy = 98.06%). While the factors that are important for matching recommendations consists of 9 factors: policies of the organization, vision of the organization, mission of the organization, experience and achievements of researchers, qualifications of research team, interest in the research topics, impressions and examples in the past, technology and laboratory support, and budget support. For the future, the researchers are aimed to research on the development of students’ academic achievement and aims to promote a learning culture based on the results of this research.
Performance Analysis of Grid-Connected PV Rooftop, at Sakon Nakhon Province, Thailand
Supalak Sathiracheewin, Patamaporn Sripadungtham, Settakorn Kamuang
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 816-823 (2020);
View Description
The performance ratio (PR) based on IEC 61724 standard is calculated under the influence of seasonal variations and the capability of the system. On the other hand, The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) of the U.S. Department of Energy proposed the weather-corrected performance ratio (PRcorr). This PRcorr index calculates the performance of the PV system which has taken the weather variations that influence the cell temperature into account. Both techniques were compared with the simulation program to analyze the PR index according to system conditions. The study site is the on-grid PV rooftop at Kasetsart University Chalermphakiat Sakon Nakhon (CSC). The PV panel is oriented to the southwest, 215 degrees azimuth. The angle of the inclination of the panel is 17 degrees. The result shows the trend of monthly PRcorr with little variations. At the same time, the PR value over the year has a lot of variations. The variation of PRcorr and PR is 2.39 and 5.07, respectively. PRcorr has low variability due to the correction of weather factors. The average cell temperature is an important variable. To calculate the average temperature of the panels, one year of data is needed to filter out distorted information. The system available condition is an important factor for the on-grid PV system at low voltage.
Fine Tuning the Performance of Parallel Codes
Sanaz Gheibi, Tania Banerjee, Sanjay Ranka, Sartaj Sahni
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 824-840 (2020);
View Description
We propose a multilevel method to speed highly optimized parallel codes whose runtime increases faster than their workload. This method requires the ability to solve large in- stances by decomposing them into smaller instances. Using a simple parallel computing model, we derive a mathematical model that predicts whether or not our method can im- prove performance and also predicts the amount of improvement attainable. Our method is tested and shown to be effective on three highly optimized BLAS (Basic Linear Alge- bra Subprograms) routines from Intel’s Math Kernel Library (MKL). Those routines are cblas dgemm, cblas dtrmm and cblas dsymm. On the Intel Knights Landing (KNL) platform our method speeds cblas dgemm by 33%, cblas dtrmm by 50% and cblas dsymm by 49% on double-precision matrices of size 16K x 16K, when the KNL’s default memory-clustering configuration (cache-quadrant) is used.
Generic Decision Support Model for Determining the Best Marketer
Ditdit Nugeraha Utama, Sherly Oktafiani
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 841-848 (2020);
View Description
For marketing company, determining the best marketing is a strategic decision. It is able to affect the companys future purposefully. The study conducted to propose a novel decision support model (DSM) for determining the best marketer. Seventeen parameters were considered into model and two methods fuzzy logic and profile-matching (PM) were combined as main method in constructing the model theoretically. The model was applied in medical appliance marketing company. It is finally also able to measure and present the that is able to make company for easily making a crucial decision.
Design of Aerial Panoramic Photography: Contrast between Industrialized and Natural Zones
Wei Zhong Feng, Yu-Che Huang, Fang-Lin Chao
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(4), 849-856 (2020);
View Description
This study utilized aerial panoramic photography and 3D virtual reality to demonstrate the environmental changing issues. Environmental problems have occurred in the surroundings for a long time, but the public has gradually become numb. The wide view through aerial photography helps to show the difference. The proposed self-assembled drone equipped with an antishock bracket containing a six-axis aerial camera was used to capture videos with the critical environmental problems in Taiwan. The captured panoramic video was processed using post-production software to create a unique documentary revealing the adverse effects of pollution. The video portrayed a sharp contrast between the eastern and western coastline of Taiwan by presenting planet images. Most participants of a survey reported increased awareness of environmental protection after watching the aerial panoramic films.

