A Framework for Measuring Workforce Agility: Fuzzy Logic Approach Applied in a Moroccan Manufacturing Company
Volume 5, Issue 3, Page No 411-418, 2020
Author’s Name: Fadoua Tamtama), Amina Tourabi
View Affiliations
National School of Applied Sciences, Systems Engineering and Decision Support Laboratory, 80000, Morocco
a)Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: fadoua.tamtam@gmail.com
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 5(3), 411-418 (2020); ![]() DOI: 10.25046/aj050352
DOI: 10.25046/aj050352
Keywords: Workforce agility, Fuzzy logic, Agile enablers
Export Citations
In today’s Moroccan business environment, companies need to implement organization agility by developing an agile workforce that is able to deal with the environment volatility. Thus, the agile workforce concept has been appeared as a necessary and sufficient condition to achieve agility. Focusing on agile enablers influencing workforce agility is an important area but currently there is limited literature available. Acknowledging its importance, we continued our literature exploration in order to identify the enablers of workforce agility. Then, we describe a list of four enablers with different criteria and attributes. This paper further proposed fuzzy logic approach to evaluate different measures of the workforce agility. The results suggest that engagement, knowledge sharing, acceptance of changes and self-motivation are the most important attributes of agile workforce. Apart from that, different agile workforce attributes need to be improved in order to achieve the extremely agile level of the workforce.
Received: 03 May 2020, Accepted: 22 May 2020, Published Online: 11 June 2020
1. Introduction
This paper is an extension of work originally presented in 4th World Conference on Complex Systems (WCCS) [1].
For many years, unexpected and dynamic changes [2] represent a common reality facing many organizations from different sizes and sectors. This volatility makes traditional approaches useless for fulfilling current organizational goals. Under this pressure [3], enterprises need to implement agility in order to achieve profitability [4]. The agility means the ability to quickly respond and adapt to volatile market environments. According to the different definitions of “agility” proposed in the literature [2], agility includes different competitive criteria like speed, flexibility, innovation, adaptability, proactivity, quality, productivity, profitability, customization, and knowledge [3] which help to focus on products and services driven by customer instead of those driven by the company [5].
The successful implementation of agility requires adapting all enterprise elements such as goals, technology and people to the unexpected changes [2]. Thus, agility concept has been extended to cover different organization areas. Within this paper [5], the term workforce agility appeared as the employee ability to adapt and evolve quickly by providing innovative solutions to different problems during any phase of the company project/program. Therefore, agile workforce needs to exhibit sufficient skills [6] which have been implicitly mentioned in Zhang and Sharifi [7] definition: Agile workforce is knowledge worker [3] with a broad vision and who is able to deal with environmental turbulence by capturing the advantageous side of these changes [8]. The same definition was presented by others researchers like Breu, et al. [5] who defined the concept as environmental responsiveness to market volatility [9], also Patil and Suresh [6] defined it as the ability to respond to customer needs and uncertain changes within the stipulated time.
From the literature review, the agile workforce is an essential facet of the overall agility level of the organization [3] since it allows to achieve different organizational benefits [5]. However, there was less focus on the theoretical and empirical validation of workforce agility enablers [5]. The main aim of the present paper is to identify the crucial factors influencing the workforce agility [6]. The following section develops a list of four workforce agility enablers by identifying their criteria and attributes from the literature [5].
2. Literature review: Enablers of the agile workforce
After reviewing the literature, four enablers have been identified as important factors playing a crucial role in improving the workforce agility.
Individually, to be agile, the workforce needs to be adaptable or flexible. Then, an agile workforce needs to be proactive [6], which means self-anticipating the activities influencing positively the changes [2]. Also, workforce with innovative behavior is an agile workforce who can identify the need for a new product/service/process/technology or improving those existing.
From what was mentioned previously, the workforce handles multiple tasks or programs simultaneously, which means the workforce needs to focus on the most important ones for his work. If the working conditions are stressful, the workforce should be resilient. Other behaviors should be demonstrated by the agile workforce as getting knowledge of marketplace, business environment, organization operations and future priorities. These behaviors are grouped under the name business orientation. Also, it is important for agile workforce to achieve multiple competencies as those related to management, business process change, technical [6], information technology or software which were identified by Breu et al. [5,6]. Other researchers have identified responsiveness and intelligence as the main attributes of agility. Also, highly motivated and informed workforce is beneficial for the organization success.
Collectively, agile workforce needs to cooperate and share knowledge with internal or external groups which ensures fluid information, communication and knowledge flow across these groups which is important for agile team [6].
Table 1 summarizes enablers, criteria and attributes discussed in the workforce agility literature [5].
Table 1: Workforce agility enablers (Adapted from [2,3,6])
| Workforce agility enablers | Workforce agility criteria | Workforce agility attributes |
|
Workforce status (E1) |
Adaptability/ Flexibility (E11) |
Simultaneously work on multiple work assignments within program or across different groups in organization (E111) |
|
Move quickly from role to role, to new tasks and responsibilities (E112) |
||
|
Engage and disengage often and easily with others with a singular focus on task accomplishment as per requirement (E113) |
||
|
Having interpersonal and cultural adaptability (E114) |
||
|
Acquire skills of professional flexibility (E115) |
||
|
Constant and quick learning of new skills, technologies, and procedures (E116) |
||
|
Acceptance rate of the workforce to altered working time or work locations (E117) |
||
|
Competency/ Self-awareness (E12) |
Developing new skills or competencies within a short span (E121) |
|
|
Developing new skills in business process change (E122) |
||
|
Developing new management skills (E123) |
||
|
Developing new technical skills (E124) |
||
|
Developing new skills in information technology (E125) |
||
|
Developing new software skills (E126) |
||
|
Comprehension of new ideas, knowledge, or technologies (E127) |
||
|
Creativity and innovation in problem-solving (E128) |
||
|
Workforce autonomy (E2) |
Proactivity (E21) |
Dynamically explore new opportunities (E211) |
|
Identify and anticipate problems related to change (E212) |
||
|
Accomplish the promising goals (E213) |
||
|
Personal initiative (E214) |
||
|
Solution of the change related problems (E215) |
||
|
Innovation (E22) |
Continuously work towards gaining proficiency in multiple competency areas (E221) |
|
|
Share the gained knowledge with its partners and collaborators (E222) |
||
|
Exploring into new markets (E223) |
||
|
Generates new ideas to tackle the unidentified change requests made by customers (E224) |
||
|
Generates new ideas to come out of the ambiguous situations faster (E225) |
||
|
Resiliency (E23) |
Taking calculated risks (E231) |
|
|
Coming out comfortably from ambiguous situations quickly (E232) |
||
|
Positive attitude to change, to new ideas and technology (E233) |
||
|
Tolerance to stressful and uncertain situations (E234) |
||
|
Intelligence/ Responsiveness [6] (E24) |
Quick response to changing customer needs and market conditions (E241) |
|
|
Sensing changes (E242) |
||
|
Execute things smoothly (E243) |
||
|
Quickness/ Speed (E25) |
Shorter transition or recovery time (E251) |
|
|
Faster completion time (E252) |
||
|
Products or services delivery speed (E253) |
||
|
Problem-solving speed (E254) |
||
|
Workforce job (E3) |
Focus (E31) |
Set priorities while handling multiple programs (E311) |
|
Set priorities to drive towards solutions (E312) |
||
|
Demonstrate a strong sense of urgency to deliver a set goal (E313) |
||
|
Demonstrate right focus (E314) |
||
|
Business Orientation (E32) |
Get knowledge of marketplace (E321) |
|
|
Get knowledge of business environment (E322) |
||
|
Get knowledge of the organization’s operations (E323) |
||
|
Get knowledge of future priorities (E324) |
||
|
Get aligned with the organizational values (E325) |
||
|
Informative (E33) |
Serious information seekers (E331) |
|
|
Keep informed in order to achieve the objectives or clarify problems (E332) |
||
|
Personally undertake research, analysis or investigation (E333) |
||
|
Use contacts or information networks to obtain useful information about technologies and processes related to programs they are working on (E334) |
||
|
Workforce involvement (E4) |
Collaboration (E41) |
Ability to collaborate with other teams, functions and organizations (E411) |
|
Avoid duplication of efforts (E412) |
||
|
Use decision-makers from different domains (E413) |
||
|
Smooth flow of knowledge and information across the boundaries of groups (E414) |
||
|
Willingness to enter unexpected collaborations (E415) |
||
|
Tolerance to different or new opinions of people from other disciplines (E416) |
||
|
Tolerance to different or new approach in collaboration (E417) |
||
|
Ease of communication (E418) |
||
|
Autonomy in collaboration (E419) |
||
|
Self-motivation/ Ownership (E42) |
Self-motivation for seeking solutions to change issues (E421) |
|
|
Workforce needs possibility of growth (E422) |
||
|
Workforce needs recognition (E423) |
||
|
Workforce needs advancement (E424) |
||
|
Workforce needs technical supervision (E425) |
||
|
Pursue goals in the face of setbacks (E426) |
3. Fuzzy logic approach to measure workforce agility of a Moroccan company
Acknowledging the importance of workforce agility, it has been assessed through several means such as [10] fuzzy logic, exploratory methodology, descriptive statistics, mathematical modeling and discriminate analysis [11].
Due to the ill-defined and vague indicators which exist within agility assessment [12], the decision-makers are unable to make a significant measurement when available information is scarce [13]. Thus, fuzzy logic has been widely used to handle real-life problems which are subjective, vague, and imprecise in nature [14]. These phenomena can be assessed only by linguistic values rather than numerical terms [13]. Using fuzzy concepts, each linguistic term can be associated with membership function [12]. When it is easy to determine an exact membership function we can use only type-1 fuzzy logic system, which means in our circumstances we don’t need to evaluate the workforce agility measures by type-2 fuzzy logic system.
4. Fuzzy logic application
4.1. About the company
The proposed assessment has been done for an industrial company (hereafter referred as Indus_Comp) at southern part of Morocco [15]. Indus_Comp was started in 1999 and it designs and develops products dedicated to individual homes and professional projects. Currently Indus_Comp faces the challenges of modernization and competition and it should be able to offer an unlimited choice of products and service. In order to sustain in this agile environment, Indus_Comp needs to identify the weaker enablers [12] which can affect its competitive positioning.
In this context, and according to the hierarchical composition of the company, a questionnaire has been distributed to five decision-makers of Indus_Comp. The collected data are provided below [15].
4.2. Results and discussion
Each decision-maker has been instructed to express the suitable linguistic variables (Table 2) in terms of importance weight and performance rating against each agile workforce attribute. The linguistic scale has been furnished in Table 3. Then, these linguistic variables have been converted into fuzzy intervals (Table 4). The next step is to calculate the aggregated importance weights and aggregated performance ratings of the agile workforce criteria and enablers (Table 5). Finally, we obtained the fuzzy workforce agility index and fuzzy performance importance index of all the attributes (FPII) [15]. A detailed description of fuzzy logic application is given as follows [16]:
- Step 1: Identification of agile workforce enablers, criteria and attributes [17]: From the literature, four enablers, twelve criteria and sixty-four attributes were identified (Table 1).
- Step 2: Collection of performance rating and importance weights of agile workforce attributes: Five decision-makers (DM1, DM2,…, DM5) from Indus_Comp were asked to provide the required detail [15] in terms of linguistic variables (Table 2).
Table 2: Fuzzy calculation of agile workforce enablers
| Agile Workforce attributes | Importance weight | Performance rating | ||||||||
| DM1 | DM2 | DM3 | DM4 | DM5 | DM1 | DM2 | DM3 | DM4 | DM5 | |
| E111 | M | H | M | VL | VL | G | F | F | F | VP |
| E112 | H | H | FH | FH | H | G | F | F | F | VG |
| E113 | M | H | FL | M | M | VG | E | F | G | G |
| E114 | M | M | M | M | M | F | F | F | G | G |
| E115 | H | M | FH | M | FH | F | F | G | VG | VG |
| E116 | H | FH | M | H | FH | P | F | P | G | F |
| E117 | FH | H | FH | M | FH | W | W | P | F | P |
| E121 | H | H | M | FH | H | W | W | VP | F | F |
| E122 | M | H | H | FH | H | G | VG | E | E | G |
| E123 | VH | H | H | VH | H | G | F | G | G | VG |
| E124 | H | FH | H | FH | FH | E | E | G | F | E |
| E125 | H | FH | H | FH | H | G | G | G | VG | G |
| E126 | FH | M | FH | M | FH | F | G | F | F | G |
| E127 | H | M | M | M | H | G | G | G | VG | F |
| E128 | VH | H | H | VH | VH | VP | F | P | P | G |
| E211 | H | FH | M | FH | H | W | F | G | F | G |
| E212 | H | H | H | FH | H | G | VG | G | F | F |
| E213 | FH | M | FH | FH | M | W | W | F | G | VP |
| E214 | FH | FH | FH | FH | FH | VP | P | P | F | P |
| E215 | VH | H | H | VH | H | F | G | E | VG | E |
| E221 | H | FH | H | FH | FH | VP | P | W | F | F |
| E222 | FL | M | FL | FL | M | VG | F | E | F | G |
| E223 | H | FH | H | M | FH | W | VP | G | E | G |
| E224 | H | M | M | FH | H | VP | F | F | W | E |
| E225 | FH | H | H | H | FH | F | G | E | VG | G |
| E231 | H | FL | H | M | H | F | F | VG | F | G |
| E232 | M | M | FH | H | FL | G | E | F | G | F |
| E233 | H | VH | FH | FL | FL | E | VG | G | E | E |
| E234 | VH | M | VH | H | VH | VP | P | P | W | G |
| E241 | H | FH | VH | H | H | VP | G | E | G | G |
| E242 | H | FH | M | H | M | F | VG | VG | G | VG |
| E243 | FH | FH | FH | FH | FH | VP | VG | F | G | F |
| E251 | FH | M | FH | FH | M | W | W | VP | F | VP |
| E252 | H | FH | H | FH | M | G | F | G | VG | E |
| E253 | H | M | FH | H | H | W | W | G | F | G |
| E254 | FH | M | H | FH | FH | VP | P | W | P | F |
| E311 | H | FH | H | FH | M | G | F | P | VP | G |
| E312 | FH | FH | H | FH | H | P | W | F | G | P |
| E313 | H | H | H | H | H | W | W | F | F | P |
| E314 | VH | H | VH | VH | H | F | G | P | P | P |
| E321 | FH | H | FH | M | FH | E | VG | G | E | F |
| E322 | H | H | H | H | H | E | E | VG | F | F |
| E323 | FH | M | H | H | H | P | F | F | G | VG |
| E324 | H | FH | H | H | M | E | VG | G | F | G |
| E325 | H | H | H | H | H | E | F | G | F | F |
| E331 | H | M | M | M | M | W | W | F | G | F |
| E332 | FH | FH | H | H | FH | W | P | VP | G | F |
| E333 | H | FH | FH | H | H | E | E | E | G | E |
| E334 | H | M | FH | M | H | VP | P | F | G | F |
| E411 | H | FH | FH | FH | M | F | G | P | F | G |
| E412 | H | FH | H | FH | M | F | E | VG | G | F |
| E413 | H | FH | FH | H | H | G | F | F | E | G |
| E414 | H | H | FH | H | M | VP | F | F | F | F |
| E415 | FH | M | M | FH | FH | E | G | G | F | F |
| E416 | H | FH | H | FH | FH | G | E | F | F | VG |
| E417 | M | M | M | FH | FH | W | W | W | F | P |
| E418 | H | M | FH | FH | H | E | E | E | E | VG |
| E419 | H | FH | H | H | H | E | VG | F | P | F |
| E421 | M | H | M | M | FH | VG | G | F | E | E |
| E422 | FH | FH | M | M | H | W | G | P | F | F |
| E423 | H | M | M | M | FH | G | F | G | E | F |
| E424 | FH | H | H | H | H | G | F | F | F | VG |
| E425 | M | H | FH | H | H | E | G | F | P | VP |
| E426 | FH | H | M | H | FH | W | VP | P | VP | F |
- Step 3: Matching the linguistic terms with the corresponding fuzzy intervals [16,17]: Table 3 presents linguistic terms and its appropriate fuzzy numbers for weight and ratings assignment [15] chosen from literature [10,16] .
Table 3: Fuzzy intervals for approximating linguistic terms (Adapted from [16])
| Importance Weight | Performance Rating | ||
| Linguistic variable | Fuzzy number | Linguistic variable | Fuzzy number |
| Very Low (VL) | (0, 0.05, 0.15) | Worst (W) | (0, 0.5, 1.5) |
| Low (L) | (0.1, 0.2, 0.3) | Very Poor (VP) | (1, 2, 3) |
| Fairly Low (FL) | (0.2, 0.35, 0.5) | Poor (P) | (2, 3.5, 5) |
| Medium (M) | (0.3, 0.5, 0.7) | Fair (F) | (3, 5, 7) |
| Fairly High (FH) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | Good (G) | (5, 6.5, 8) |
| High (H) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | Very Good (VG) | (7, 8, 9) |
| Very High (VH) | (0.85, 0.95, 1.0) | Excellent (E) | (8.5, 9.5, 10) |
- Step 4: Application of fuzzy calculations on the weight and rating of each agile attribute, criteria and enabler. First, we calculate the average fuzzy weight and average fuzzy performance rating of each agile attribute [10] as shown in the following example.
E111 average fuzzy weight = [M+H+M+VL+VL]/5 = (0.3, 0.5, 0.7)/5, (0.7, 0.8, 0.9)/5, (0.3, 0.5, 0.7)/5, (0, 0.05, 0.15)/5, (0, 0.05, 0.15)/5 = (0.26, 0.38, 0.52)
E111 average fuzzy performance rating = [G+F+F+F+VP]/5 = (5, 6.5, 8)/5, (3, 5, 7)/5, (3, 5, 7)/5, (3, 5, 7)/5, (1, 2, 3)/5 = (3.0, 4.7, 6.4)
Then, we calculate the rating of each agile criterion [10]. An example of this calculation is demonstrated below.
Example: Rating of the criterion E11=
[(3.0, 4.7, 6.4) Ä (0.26, 0.38, 0.52) Å (4.2, 5.9, 7.6) Ä (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) Å (5.7, 7.1, 8.4) Ä (0.36, 0.53, 0.70) Å (3.8, 5.6, 7.4) Ä (0.3, 0.5, 0.7) Å (5.0, 6.5, 8.0) Ä (0.46, 0.62, 0.78) Å (3.0, 4.7, 6.4) Ä (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) Å (1.4, 2.6, 4.0) Ä (0.50, 0.65, 0.80)] / [(0.26, 0.38, 0.52) Å (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) Å (0.36, 0.53, 0.70) Å (0.3, 0.5, 0.7) Å (0.46, 0.62, 0.78) Å (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) Å (0.50, 0.65, 0.80)] = (3.68, 5.27, 6.87)
Table 4: Fuzzy calculation of the criteria rating
| Agile workforce criteria | Agile workforce attributes | Average fuzzy performance rating | Average fuzzy weight | Criteria rating |
| E11 | E111 | (3.0, 4.7, 6.4) | (0.26, 0.38, 0.52) | (3.68, 5.27, 6.87) |
| E112 | (4.2, 5.9, 7.6) | (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) | ||
| E113 | (5.7, 7.1, 8.4) | (0.36, 0.53, 0.70) | ||
| E114 | (3.8, 5.6, 7.4) | (0.3, 0.5, 0.7) | ||
| E115 | (5.0, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.46, 0.62, 0.78) | ||
| E116 | (3.0, 4.7, 6.4) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | ||
| E117 | (1.4, 2.6, 4.0) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E12 | E121 | (1.4, 2.6, 4.0) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | (4.54, 5.97, 7.37) |
| E122 | (6.8, 8.0, 9.0) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E123 | (5.0, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.76, 0.86, 0.94) | ||
| E124 | (6.7, 8.0, 9.0) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E125 | (5.4, 6.8, 8.2) | (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) | ||
| E126 | (3.8, 5.6, 7.4) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | ||
| E127 | (5.0, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.46, 0.62, 0.78) | ||
| E128 | (2.6, 4.1, 5.6) | (0.79, 0.89, 0.96) | ||
| E21 | E211 | (3.2, 4.7, 6.3) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | (2.46, 3.58 4.79) |
| E212 | (4.6, 6.2, 7.8) | (0.66, 0.77, 0.88) | ||
| E213 | (1.8, 2.9, 4.2) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | ||
| E214 | (2.0, 3.5, 5.0) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E215 | (6.4, 7.7, 8.8) | (0.76, 0.86, 0.94) | ||
| E22 | E221 | (1.8, 3.2, 4.7) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | (3.83, 5.19, 6.53) |
| E222 | (5.3, 6.8, 8.2) | (0.24, 0.41, 0.58) | ||
| E223 | (3.9, 5.0, 6.1) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | ||
| E224 | (3.1, 4.4, 5.7) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E225 | (5.7, 7.1, 8.4) | (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) | ||
| E23 | E231 | (4.2, 5.9, 7.6) | (0.52, 0.65, 0.78) | (4.49, 5.90, 7.25) |
| E232 | (4.9, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.40, 0.56, 0.72) | ||
| E233 | (7.5, 8.6, 9.4) | (0.49, 0.62, 0.74) | ||
| E234 | (2.0, 3.2, 4.5) | (0.71, 0.83, 0.92) | ||
| E24 | E241 | (4.9, 6.2, 7.4) | (0.69, 0.80, 0.90) | (4.84, 6.20, 7.53) |
| E242 | (5.8, 7.1, 8.4) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E243 | (3.8, 5.3, 6.8) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E25 | E251 | (1.0, 2.0, 3.2) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | (2.85, 4.03, 5.32) |
| E252 | (5.7, 7.1, 8.4) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | ||
| E253 | (2.6, 3.8, 5.2) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E254 | (1.6, 2.9, 4.3) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E31 | E311 | (3.2, 4.7, 6.2) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | (2.47, 3.94, 5.47) |
| E312 | (2.4, 3.8, 5.3) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E313 | (1.6, 2.9, 4.4) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | ||
| E314 | (2.8, 4.4, 6.0) | (0.79, 0.89, 0.96) | ||
| E32 | E321 | (6.4, 7.7, 8.8) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | (5.29, 6.78, 8.15) |
| E322 | (6.0, 7.4, 8.6) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | ||
| E323 | (4.0, 5.6, 7.2) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E324 | (5.7, 7.1, 8.4) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E325 | (4.5, 6.2, 7.8) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | ||
| E33 | E331 | (2.2, 3.5, 5.0) | (0.38, 0.56, 0.74) | (4.01, 5.22, 6.44) |
| E332 | (2.2, 3.5, 4.9) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E333 | (7.8, 8.9, 9.6) | (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) | ||
| E334 | (2.8, 4.4, 6.0) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | ||
| E41 | E411 | (3.6, 5.3, 7.0) | (0.50, 0.65, 0.80) | (4.62, 6.04, 7.41) |
| E412 | (5.3, 6.8, 8.2) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | ||
| E413 | (4.9, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.62, 0.74, 0.86) | ||
| E414 | (2.6, 4.4, 6.2) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E415 | (4.9, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | ||
| E416 | (5.3, 6.8, 8.2) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E417 | (1.0, 2.0, 3.3) | (0.38, 0.56, 0.74) | ||
| E418 | (8.2, 9.2, 9.8) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) | ||
| E419 | (4.7, 6.2, 7.6) | (0.66, 0.77, 0.88) | ||
| E42 | E421 | (6.4, 7.7, 8.8) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | (3.81, 5.30, 6.74) |
| E422 | (2.6, 4.1, 5.7) | (0.46, 0.62, 0.78) | ||
| E423 | (4.9, 6.5, 8.0) | (0.42, 0.59, 0.76) | ||
| E424 | (4.2, 5.9, 7.6) | (0.66, 0.77, 0.88) | ||
| E425 | (3.9, 5.3, 6.6) | (0.58, 0.71, 0.84) | ||
| E426 | (1.4, 2.6, 3.9) | (0.54, 0.68, 0.82) |
After that, we calculate the rating of each agile enabler by using the same calculation method (Table 5). For example, the rating of the enabler E1 is calculated as
E1= [(3.68, 5.27, 6.87) Ä (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (4.54, 5.97, 7.37) Ä (0.7, 0.8, 0.9)] / [(0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (0.7, 0.8, 0.9)] = (4.18, 5.66, 7.13)
Table 5: Fuzzy calculation of the enablers rating
| Agile workforce enablers | Agile workforce criteria | Criteria rating | Fuzzy importance weight of the agile workforce criteria | Enabler rating | Fuzzy importance weight of the agile workforce enablers |
| E1 | E11 | (3.68, 5.27, 6.87) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | (4.18, 5.66, 7.13) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) |
| E12 | (4.54, 5.97, 7.37) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | |||
| E2 | E21 | (4.54, 5.97, 7.37) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | (4.11, 5.46, 6.80) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) |
| E22 | (3.83, 5.19, 6.53) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | |||
| E23 | (4.49, 5.90, 7.25) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | |||
| E24 | (4.84, 6.20, 7.53) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | |||
| E25 | (2.85, 4.03, 5.32) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | |||
| E3 | E31 | (2.47, 3.94, 5.47) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | (4.08, 5.42, 6.74) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) |
| E32 | (5.29, 6.78, 8.15) | (0.7, 0.8, 0.9) | |||
| E33 | (4.01, 5.22, 6.44) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | |||
| E4 | E41 | (4.62, 6.04, 7.41) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) | (4.21, 5.67, 7.07) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) |
| E42 | (3.81, 5.30, 6.74) | (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) |
- Step 5: Calculation of the fuzzy workforce agility index of Indus_Comp [17]: Using the same calculation method, we obtained
Fuzzy workforce agility index = [(4.18, 5.66, 7.13) Ä (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (4.11, 5.46, 6.80) Ä (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (4.08, 5.42, 6.74) Ä (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (4.21, 5.67, 7.07) Ä (0.5, 0.65, 0.8)] / [(0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (0.5, 0.65, 0.8) Å (0.5, 0.65, 0.8)] = (4.14, 5.55, 6.93)
- Step 6: Matching the fuzzy workforce agility index with the appropriate linguistic label [16,17]: From the literature, we selected five linguistic labels (slowly agile, fairly agile, agile, very agile, extremely agile) (Table 6) [16]. Then, we convert the index into the suitable label using Euclidean distance method [10]. This method calculate the distance from the index to each agility level as shown below [16]:
Table 6: Linguistic labels and the corresponding fuzzy intervals (Adapted from [16])
| Level of agility | Fuzzy intervals |
| Slowly Agile | (0, 1.5, 3) |
| Fairly Agile | (1.5, 3, 4.5) |
| Agile | (3.5 5 6.5) |
| Very Agile | (5.5, 7, 8.5) |
| Extremely Agile | (7, 8.5, 10) |
D (FAI, Slowly Agile) = {(4.14‐0)2 + (5.55‐1.5)2 + (6.93‐3)2}1/2 = 7.00
D (FAI, Fairly Agile) = {(4.14‐1.5)2 + (5.55‐3)2 + (6.93‐4.5)2}1/2 = 4.40
D (FAI, Agile) = {(4.14‐3.5)2 + (5.55‐5.0)2 + (6.93‐6.5)2}1/2 = 0.95
D (FAI, Very Agile) = {(4.14‐5.5)2 + (5.55‐7)2 + (6.93‐8.5)2}1/2 = 2.53
D (FAI, Extremely Agile) = {(4.14‐7)2 + (5.55‐8.5)2 + (6.93‐10)2}1/2 = 5.13
The minimum distance between the index and the linguistic label was obtained for the “agile” label [10], as it is showed in figure 1.
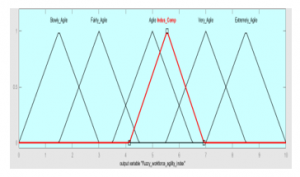
Figure 1: Fuzzy workforce agility index of Indus-Comp
- Step 7: Calculation of fuzzy performance importance index (FPII) and its score [10]: In order to improve the agility level, we calculate the FPII of each agile workforce attribute. Then, the score of each FPII represents its contribution to the agility of workforce. The score of the 64 FPIIs are presented in table 7. If the score is weak it means that the attribute doesn’t contribute to the overall workforce agility [16] and vice versa.
An example of FPII111 and its score are calculated as:
FPII111 = [(1, 1, 1) – (0.26, 0.38, 0.52)] Ä (3.0, 4.7, 6.4) = (2.22, 2.91, 3.07)
Score of FPII111 = (2.22 + 4 × 2.91 + 3.07) / 6 = 2.82
Table 7: FPII and ranking score of the agile workforce attributes
| Agile workforce attributes | FPII | Ranking score |
| E111 | (2.22, 2.91, 3.07) | 2.82 |
| E112 | (1.60, 1.53, 1.06) | 1.46 |
| E113 | (3.65, 3.34, 2.52) | 3.25 |
| E114 | (2.66, 2.80, 2.22) | 2.68 |
| E115 | (2.70, 2.47, 1.76) | 2.39 |
| E116 | (1.38, 1.50, 1.15) | 1.42 |
| E117 | (0.70, 0.91, 0.80) | 0.86 |
| E121 | (0.59, 0.75, 0.64) | 0.70 |
| E122 | (2.86, 2.32, 1.44) | 2.26 |
| E123 | (1.20, 0.91, 0.48) | 0.89 |
| E124 | (2.81, 2.32, 1.44) | 2.25 |
| E125 | (2.05, 1.77, 1.15) | 1.71 |
| E126 | (2.20, 2.30, 1.78) | 2.20 |
| E127 | (2.70, 2.47, 1.76) | 2.39 |
| E128 | (0.55, 0.45, 0.22) | 0.43 |
| E211 | (1.47, 1.50, 1.13) | 1.43 |
| E212 | (1.56, 1.43, 0.94) | 1.37 |
| E213 | (1.04, 1.19 1.01) | 1.13 |
| E214 | (1.00, 1.22, 1.00) | 1.15 |
| E215 | (1.54, 1.08, 0.53) | 1.06 |
| E221 | (0.76, 0.93, 0.75) | 0.87 |
| E222 | (4.03, 4.01, 3.44) | 3.92 |
| E223 | (1.79, 1.60, 1.10) | 1.55 |
| E224 | (1.55, 1.54, 1.14) | 1.47 |
| E225 | (2.17, 1.85, 1.18) | 1.79 |
| E231 | (2.02, 2.06, 1.67) | 1.99 |
| E232 | (2.94, 2.86, 2.24) | 2.77 |
| E233 | (3.82, 3.27, 2.44) | 3.22 |
| E234 | (0.58, 0.54, 0.36) | 0.52 |
| E241 | (1.52, 1.24, 0.74) | 1.20 |
| E242 | (2.90, 2.48, 1.68) | 2.42 |
| E243 | (1.90, 1.85, 1.36) | 1.78 |
| E251 | (0.58, 0.82, 0.77) | 0.77 |
| E252 | (2.62, 2.27, 1.51) | 2.20 |
| E253 | (1.09, 1.10, 0.83) | 1.05 |
| E254 | (0.80, 1.01, 0.86) | 0.95 |
| E311 | (1.47, 1.50, 1.12) | 1.43 |
| E312 | (1.01, 1.10, 0.85) | 1.04 |
| E313 | (0.48, 0.58, 0.44) | 0.54 |
| E314 | (0.59, 0.48, 0.24) | 0.46 |
| E321 | (3.20, 2.69, 1.76) | 2.62 |
| E322 | (1.80, 1.48, 0.86) | 1.43 |
| E323 | (1.68, 1.62, 1.15) | 1.55 |
| E324 | (2.39, 2.06, 1.34) | 1.99 |
| E325 | (1.35, 1.24, 0.78) | 1.18 |
| E331 | (1.36, 1.54, 1.30) | 1.47 |
| E332 | (0.92, 1.01, 0.78) | 0.96 |
| E333 | (2.96, 2.31, 1.34) | 2.26 |
| E334 | (1.40, 1.54, 1.20) | 1.46 |
| E411 | (1.80, 1.85, 1.40) | 1.77 |
| E412 | (2.44, 2.18, 1.48) | 2.11 |
| E413 | (1.86, 1.69, 1.12) | 1.62 |
| E414 | (1.09, 1.28, 0.99) | 1.20 |
| E415 | (2.84, 2.66, 1.92) | 2.57 |
| E416 | (2.23, 1.97, 1.31) | 1.90 |
| E417 | (0.62, 0.88, 0.86) | 0.83 |
| E418 | (3.77, 2.94, 1.76) | 2.88 |
| E419 | (1.60, 1.43, 0.91) | 1.37 |
| E421 | (3.71, 3.15, 2.11) | 3.07 |
| E422 | (1.40, 1.56, 1.25) | 1.48 |
| E423 | (2.84, 2.66, 1.92) | 2.57 |
| E424 | (1.43, 1.36, 0.91) | 1.30 |
| E425 | (1.64, 1.54, 1.06) | 1.48 |
| E426 | (0.64, 0.83, 0.70) | 0.78 |
After calculating the scores of the 64 FPIIs, the Indus_Comp management was consulted to decide the appropriate threshold in order to rank the attributes. Subsequently, threshold 1.1 was identified as the management scale [10,16], and sixteen attributes have a lower score than 1.1 (Table 7):
- Acceptance rate of the workforce to altered working time or work locations ;
- Tolerance to different or new approach in collaboration ;
- Creativity and innovation in problem-solving [3].
- Developing new skills or competencies within a short span ;
- Developing new management skills ;
- Continuously work towards gaining proficiency in multiple competency areas ;
- Shorter transition or recovery time ;
- Products or services delivery speed ;
- Problem-solving speed ;
- Set priorities to drive towards solutions ;
- Demonstrate a strong sense of urgency to deliver a set goal ;
- Demonstrate right focus ;
- Keep informed in order to achieve the objectives or clarify problems ;
- Pursue goals in the face of setbacks [6].
- Solution of the change related problems ;
- Tolerance to stressful and uncertain situations [2].
5. Conclusions
Our purpose was evaluating workforce agility. In the theoretical part we presented a conceptual model including four enablers, namely workforce status, workforce autonomy, workforce job and workforce involvement. In the empirical part we used the fuzzy logic. First, we collected data from decision-makers, then selected the appropriate fuzzy numbers for interpreting the linguistic variables, and calculated the fuzzy workforce agility index. Based on Euclidean distance computation, the workforce of Indus_Comp was agile. However, by calculating FPII and ranking different scores we identified the attributes needing some improvement so that the workforce of Indus_Comp could be extremely agile.
The contribution of this work is to help the companies to evaluate their existing level of the workforce agility by using the fuzzy logic. This method has take into account the ambiguity of each workforce agility enabler in order to calculate the overall workforce agility index. Then, the company could compare this index with that of competitors in order to identify its workforce attributes strengths and weaknesses.
Despite the above benefits, there are some limitations: In our case, the fuzzy logic depends mainly on the decision-maker only (one parameter) which excludes other employees perception who will have more detail on the technological or technical workforce attributes. Thus, taking into account other parameters can give a better tuning of results. Also, this method needs to be computerized in order to reduce time and errors that may be done in the calculation [15] or even to integrate the results provided by the fuzzy logic with other computing schemes like QFD (Quality Function Deployment), TISM (Total Interpretive Structural Modeling)…etc. For further research, this study should be conducted in different organizations of different sizes and sectors in order to carry out a comparative study. Apart from this, our conceptual model for workforce agility evaluation could also be extended in order to include other workforce aspects.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the National Centre for Scientific and Technical Research (CNRST) under the Excellence Research Scholarships Program.
- F. Tamtam, A. Tourabi, “Agile capabilities in Moroccan companies: Criteria and practices,” in 2019 4th World Conference on Complex Systems (WCCS), Ouarzazate, Morocco, 2019. https://doi: 10.1109/ICoCS.2019.8930721
- B. Sherehiy, W. Karwowski, “The relationship between work organization and workforce agility in small manufacturing enterprises,” International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 44(3), 466–473, 2014. https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2014.01.002
- R. Qin, D. A. Nembhard, “Workforce agility in operations management,” Surveys in Operations Research and Management Science, 20(2), 55–69, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sorms.2015.11.001
- R. Qin, D. A. Nembhard, “Workforce agility for stochastically diffused conditions—A real options perspective,” International Journal of Production Economics, 125(2), 324–334, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.01.006
- K. Breu, C. J. Hemingway, M. Strathern, D. Bridger, “Workforce agility: the new employee strategy for the knowledge economy,” Journal of Information Technology, 17(1), 21–31, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1080/02683960110132070
- M. Patil, M. Suresh, “Modelling the enablers of workforce agility in IoT projects: a TISM approach,” Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 20(2), 157–175, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-019-00208-7
- Z. Zhang, H. Sharifi, “A methodology for achieving agility in manufacturing organisations,” International Journal of Operations & Production Management, 20(4), 496–513, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443570010314818.
- A. Muduli, “Exploring the facilitators and mediators of workforce agility: an empirical study,” Management Research Review, 39(12), 1567–1586, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-10-2015-0236
- C. L. Bosco, “The relationship between environmental turbulence, workforce agility and patient outcomes,” Ph.D Thesis, The University of Arizona, 2007.
- M. Suresh, R. Patri, “Agility assessment using fuzzy logic approach: a case of healthcare dispensary,” BMC Health Services Research, 17(1), 394, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-017-2332-y
- S. Alavi, D. Abd. Wahab, N. Muhamad, B. Arbab Shirani, “Organic structure and organisational learning as the main antecedents of workforce agility,” International Journal of Production Research, 52(21), 6273–6295, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2014.919420
- S. Vinodh, S. R. Devadasan, B. Vasudeva Reddy, K. Ravichand, “Agility index measurement using multi-grade fuzzy approach integrated in a 20 criteria agile model,” International Journal of Production Research, 48(23), 7159–7176, 2010, https://doi.org/10.1080/00207540903354419
- C.-S. Tsai, C.-W. Chen, C.-T. Li, “Align agile drivers, capabilities and providers to achieve agility: a fuzzy-logic QFD approach,” in Supply Chain, V. Kordic, Ed. I-Tech Education and Publishing, 2008.
- C. K. M. Lee, C. T. Y. Ru, C. L. Yeung, K. L. Choy, W. H. Ip, “Analyze the healthcare service requirement using fuzzy QFD,” Computers in Industry, 74, 1–15, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2015.08.005
- S. S. K. Sahu, “Agility evaluation in fuzzy environment,” BTech Thesis, National Institute of Technology, 2013.
- C.-T. Lin, H. Chiu, Y.-H. Tseng, “Agility evaluation using fuzzy logic,” International Journal of Production Economics, 101(2), 353–368, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2005.01.011
- M. Deksnys, “Organizational agility in high growth companies,” Ph.D Thesis, Mykolas Romeris University, 2018.
