Communication Management of Digital Information Data in Human Resources as a Policy Making Strategic Program for University
Volume 4, Issue 4, Page No 539-544, 2019
Author’s Name: Edi Suryadia)
View Affiliations
Department of Office Management Education, and Communication Science Faculty of Business Economics Education, Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, 40154 West Java Indonesia.
a)Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: edi_suryadi@upi.edu
Adv. Sci. Technol. Eng. Syst. J. 4(4), 539-544 (2019); ![]() DOI: 10.25046/aj040465
DOI: 10.25046/aj040465
Keywords: Communications, Human Resources, Policy Maker, Strategic University
Export Citations
Modern universities aim at carrying capacity human resources component in its tri dharma (Three Pillars of Higher Education). UPI with sufficient conditions in the management of several resources has undoubtedly tried to establish itself as a modern university. The superior human resource support in every competition and the university’s tri dharma is the primary resource of UPI. The results of all HR roles have become inputs for the management of digital data and information. Therefore, communication management containing the university’s strategic policies can be effectively and promptly translated as well as implemented by human resources. To conduct dissemination and sustainability both nationally and internationally, this research formulated three main components in managing policy communication on human resources in a modern university, which include: (a) architecture vision, (b) value change; (c) flow diagrams, all of which refer to the achievement of vision and mission.
Received: 13 July 2019, Accepted: 15 August 2019, Published Online: 25 August 2019
1. Introduction
Universities comprise of many ranking systems such as webometrics, Q-Start, and many more. These systems can also be categorized according to specific parameters which constitute the institution’s education system and wealth of knowledge required for students to compete with other educational schools across the globe. These mutual competitions create an impact on the policy of each institution respectively. The need for higher educational level has continuously evolved with the need for leaders to obtain data and information from all university resources, especially those with available human resources. A qualified human resource condition can be a source of honesty policy with target program performance and some functional institutional ranking parameters.
The above phenomenon cannot be separated from what has been conducted by Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia (UPI). With the new leadership, UPI has begun to launch Operational Standards and Work Procedures [1] and the establishment of new university tools capable of boosting and penetrating the parameter and certification systems of higher institutions in Indonesia, Southeast Asia, and even the World. UPI’s strategy in maintaining and improving these ranking parameters is applicable at the national and international levels.
Some achievement supported by the human resources owned by UPI has been internationally recognized with a good number carried out by correlating MoU with some Western universities. UPI has been able to display some level of solidity in facilitating lecturers to conduct research. At the time of this study, about 3500 research titles had already been completed by UPI lecturers within the last three years [2]. A look at the statement indicates that during the university’s communication management some managerial facets underwent transition. Therefore, a critical analysis is required for the administration, to produce strategic communication. This happens to be one of the main focuses and reason why the research is continuously conducted at all levels.
Lecturers and students achievement were appreciated and the policy strategy, a manifestation of the UPI vision with the slogan “Leading and Out Standing”[3]. The existing communication management skills are expected to realize Sustainability University in the future. In this study, UPI will be able to strengthen the wrong policies and the programs of achievement of sustainable human resource development. Based on the above explanation, the research focuses on analyzing the Digital Information Data Communication Management Study in the form of Architecture Vision, Value Chain, and Flow Diagram within the Directorate of Human Resources in using UPI in Modern University.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Communication Management of Modern University
The study of communication management plays an essential role in education. It is the main character of a university intending to penetrate the modern reputation. [4] Explains the relationship between the world of education and communication science, as follows:
”Education and communication management influence the energy levels of change and improvement. Strong communications keep everyone focused on goals and priorities while providing feedback on progress and the required course corrections. Effective communication strategies, systems, and practices have a huge and direct effect on an organization’s learning and innovation.”
If viewed from the institutional systems owned by UPI in current time, especially with the new SOTK (an Organizational Structure and Work Procedure of UPI), some shifts concerning basic tasks and functions will be slightly different from those obtained between 2010-2015 [1]. The differences are seen from the UPI and Vice-Rectors for Academic and Student Affairs, Vice Rector for Finance and Resources, Vice Rector for Planning and Facilities, and Vice-Rector for Research and International Relations. When viewed from the leadership and UPI’s organizational structure from 2016-2020, it is clearly in transition, and requires a common understanding of the elements involved, especially in terms of the university’s internal environment management [3]. As the largest university in Indonesia, even Southeast Asia can be the best, especially if the track record of its management journey is quite dynamic. Some experts are very interested in UPI’s ability to transform from its status as a regular PTN (government university) to PTN BHMN (a government university and a law bureau of government), PT BHMN and eventually became PTN BH (government university and a law bureau).
UPI as a university is the incarnation of ex-IKIP LPTK trained achievers. It utilizes a dual curriculum characteristic comprising of educated and non-educated people with qualified human resources. Results of the previous research indicate that the UPI eventually adopted a layered model for its educational purposes [5]. This means that it follows the educational and non-education strategy with the graduate having a certificate of teaching, while the non-educational graduates, must take some educational courses. The success is inseparable from the qualifications of human resources.
If viewed from the perspective of human resources, finances, assets, and educational services, UPI students will undergo a transition period or development from the “technical service” unit to “Directorate.” Even in the current educational path, it has implemented a “Department” owned by each faculty. According to William Bridges [6], the transition management should indulge in managerial renewal and immediately regain and reintroduce the three-phase energy in its organizational life cycle, which includes (1) dreaming back dreams; (2) restoring the spirit of work; And (3) reorganizing the organization.
2.2. Strategy Formulate Performance Assessment System
Strategic management is an anticipated manageria technique which can be realized in organizational leadership. Many strategies have been played to implement the right UPI strategy in the practice of university leadership management. However, the results tend to vary with the numerous changing demands of society. [7], the strategic management process includes four essential elements: (1) environmental attenuation; (2) Strategy formulation; (3) implementation of the strategy; and (4) evaluation and control.
Communication Management deals with how leaders who become top managers analyze their needs and human resources. This effort is important because in managing an organization, leaders tend to adopt behavioral styles which grow and develop concerning a specific form and color management. Based on this phenomenon, [7] responded with a study called Policy Development, according to him, “Management now has to establish policies to determine the basic rules to be implemented in the University. These policies will guide the decision-making process in the organization. Of course, all must be supported by an accurate data information system, therefore, the existence of a management information systems owned by the University will be essential. As explained by [8], SIM is rationally integrated, i.e., a collection of semi-separated information systems integrated through activities relating to each other and primarily carried out by passing data between Systems.
Through the support of digital data and with the formulation of human resource management, a quality digitalized university will be achieved. In this case, [9] explains:
“Virtual community is an aggregation of individuals who interact around a shared interest. While this definition strips the world of its usually understood meaning, it is in accordance with the business world.”
In the context of UPI which has some business field of education, the formation of virtual academic is very appropriate, thereby, making it a virtual or digital university.
2.3. Digital Resource Information Data of the University
A campus designed with the utilization of ICT facilities in the hope of all communities, considering the fact that future educational institutions should be able to be accessed quickly and easily by the wider community. No distance and space prevent people in need of academic services. All management policies on digital campuses are expected to build up for future generations. Starting from the present generation, UPI has begun to socialize its educational services digitally[10]. This comprises of the digital implementation of new enrollment techniques, student guidance services, learning monitoring and evaluation system[2]. In practice, all academic community has started to migrate its services. Starting from employing lecturers and management with the ability to utilize digital tools and facilities.
Some foreign universities such as those in the UK, Cambridge University, Texas University, California University, Ohio University, have been making use of digitalized campus system since 1997[11]. [11] Further explained that:
“Digital generation is distinct from others in terms of its technological process as opposed to its old analog processing method.”
From the above statement, it can be deduced that the digital generation born after the non-digital or analog period fades away, thereby, contributing to its success. People in the analog period are trying to be more effective in carrying out their educational responsibilities duties by utilizing digital systems. In the context of research on UPI policy management, digital concepts can be applied to all UPI academic community which in 2 decades has been able to utilize these systems [12],[13] to support the implementation of its management functions.
In this study, several important studies on strategic communications management regarding human resources of a university are expected to be able to find new formulations to assist in the success of university quality achievement programs. The study of effective policy communication management [13] will undoubtedly be an important study of stakeholders in higher education environments. As explained by [4],:
Effective communication strategies, systems, and practices: (a) Deliver clear and consistent messages to all parts of an organization; (b) Are simple, direct, and fast with a minimal number of filters and interpreters; (c) Inspire and energize; (d) Are user-friendly, human, and personal; (e) provide information, experiences, learning ideas, direction, and feedback in all directions of an organization; (f) Provide multiple channels; (g) Are only possible in an atmosphere of trust.
From the above opinion, the main factor of the effective strategic management with regards to the Strategic Communication System [14] will be able to provide clarity as follows: (a) Deliver a clear and consistent message to all parts of the organization, (b) Deliver what is simple, direct, and fast with a minimal number of filters and interpreters, (c) Inspire and energize students, (d) Is user-friendly, human, and private, (e) Placement of information, experience, learning, ideas, direction, and feedback equally in all directions up, down, and throughout the organization, (f) Provide multiple channels, (g) Is it possible only in an atmosphere of trust and openness.
3. Methodology/Materials
This research will be conducted using the Qualitative approach in the form of Explanation Survey on work unit of Human Resources, Infrastructure, Finance, and Development Planning in UPI environment, concerning data, information management, and policy communication management model built in supporting the modern university[15]. Data collection is done by distributing questionnaires to members of the research with some leaders in the UPI environment. Study documentation and observation on all practice of policy communication strategy [14] conducted on UPI. Data analysis was done by descriptive qualitative data from[16].
4. Result and Findings
4.1. Design Flow Diagram Architecture Vision of HR Directorate
The need to develop a flow diagram as one of the guidelines in understanding the overall steps of work within the Directorate of Human Resources is an important step. During the analysis stage, several aspects of the needs program activities in previous years can be adequately detected [13]. The analysis results achieved during the Plan and Development process have obtained some participants utilized as a source of input team of the UPI human resources. Each flow diagram is intended to provide clarity on the primary task of each unit and sub-unit existing within the Directorate of Human Resources UPI.
The development forms associated with data processing and digital information has been in existence universities located in Indonesia, with several types of internal management website[17] built, such as the model information system Human Resources Information System (SISUDAMA, Model of Information System HRD). Digital data management system related to human resources in UPI environment, starting from: (a) Management of system to fulfill human resource requirement; (b) Management of the HR data placement system of each work unit; (c) management of empowerment systems; (d) Management of a career evaluation system.
- Management of recruitment system or fulfillment of human resource needs.
After placement is conducted, it is analyzed in the unit or sub-unit where shortages are incurred. Furthermore, the method of meeting the needs of human resources is in accordance with rough treatment, opportunity, or balance of energy in each unit. The fulfillment process in addition to system-based performance is also aimed at the ability for every candidate to continue assessing if the performance to be submitted is excellent following the standards. Usually, the place or unit where the candidate or employee works provides recommendations on the assessment of available prospective resources needed in supporting all tasks of the HR unit work.
- Management of HR data unit placement system.
The management of HR data placement system is performed on all resources with each system enforced. If associated with lecturers, then the submission is made starting from the process level, to the human resources directorate called and participated in the selection process. Similarly, the needs of employees may recommend employees or staff from specific fields to help other parties.
- Management of Human Resource Development or Empowerment system.
The Directorate of Human Resources manages systems Development career applicable to the university. Through this, the career system is applied in the form of a lecturer development information system for lecturers and education personnel. Mapping tasks at the university level also do it. There are some programs aimed at becoming a benchmark for the success of the educational career development of personnel within the UPI environment, using data stored on the university page, with the address http://kepakaran.upi.edu/index.php/
Based on the results of the information system expertise, human resources, especially lecturers will obtain development services by utilizing digital data through the development information systems accessible on http://bangdos.upi.edu/. In this page, educators can undergo self-development using data information on self-development in several areas during a career at every level.
- Management of HR career evaluation system.
The evaluation system managed by the Directorate of Human Resources UPI is based on digital information, all the performance and career appraisal programs are aimed at processing Digital Lecturer Workload System. As for educational personnel processes through the Employment Assessment System, both systems are designed digitally and used online. This supportive information system is available on its website http://www.upi.edu/.
- Management of Digital Information Data of UPI. Human Resources in the framework of Embodiments of Quality of Human Resources
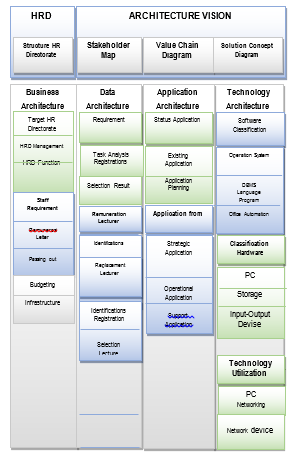 Figure 1: Architecture Vision of Communication management of Director Human Resource UPI
Figure 1: Architecture Vision of Communication management of Director Human Resource UPI
Management and resource quality improvement policies [18] are translated into programs in order to: (1) improve the quality of human resource management performance, finances, facilities and other activities that are efficient, transparent and accountable to support the enhancement of academic performance quality; (2) implementation of human resource management information system, finance, and facilities within the framework of an information management system of UPI integrated with ICT-based; (3) improves coordination effectiveness across management functions such as human resource management, finance, facilities, ICT, and other activities among work / academic units synergistically to support its performance quality; (4) improvement of quality standards for human resource management, finance and facilities oriented to international standards to meet management and / or stakeholder needs; (5) improvement of quality and / or capacity of human resources, finance, facilities and ICT; (6) development and implementation of lecturer career development system in accordance with the needs of universities and professions; (7) preparation and implementation of lecturer recruitment and / or assignment mechanism consistently; (8) improvement of effectiveness and follow-up of employee performance evaluation result (lecturer, librarian, laboratory, technician, and administration staff); (9) development and / or implementation of a fair and fair integrated compensation / remuneration system; (10) development and / or implementation of employee welfare system; (11) improvement of financial system and financial report quality improvement; (12) the implementation of performance-based budgeting policy as a form of budget adjusted to the achievements to be achieved; And (13) strengthening the function and role of the library as a teaching library [17].
Currently, human resources owned by UPI consists of lecturers and educational staff. Education personnel includes academic laboratory institutions, learning technology institutions, libraries, staffing analysts, archivists, and general functionalities. UPI lecturers amounted to 1,325 people, consisting of 1,251 government officers (PNS) and 74 non-PNS. From the findings on the management of research data relating to the Human Resources Directorate, there is a communication management model as described by the researchers in the following sections [19] [5].
From the result of analysis above, an Architecture Vision built to support the success of Human Resources Directorate of UPI, as shown in the picture below.
4.2. Value Chain of Digital Information Mobile Management HRD in UPI
From the design of communication management development above, the stages of Management Communications Policy within the Directorate of Human Resources UPI can be described as Business Modeling (Business Architecture) [20]. It is a part of the University of Education in Indonesia which aims to manage human resources by conducting tasks and functions of the main activities, such as the Recruitment CPNS, Remuneration Lecturer, Administration Letter, and Pensions CPNS. This main activity will require support from other sectors such as Administration, Finance, and Infrastructure[21]. Identification of main and supporting activities in the UPI Human Resources Directorate can be described by using the value chain of [12] shown in the following figure 2.
 Figure 2: Value Chain of HR Directorate of UPI
Figure 2: Value Chain of HR Directorate of UPI
Analyzing the thought on the review of work programs and policy communication strategies for the HR field is followed by strategic analysis [22]. From the results of this research, the needs of the HR on the assessment system for aspects of human resources as well as with Sarana is analyzed using reference sources and demands from ministry of research and higher education. Referral standard for inconsistencies relating to Educational Services, (Bureau of competence, Facilities) on human resource mapping is based on assessment center on human resources, facilities, infrastructure, and external reference documents for UPI have been developed by internal Directorate [10].
Example: Assessment System on human resources related to employment. Similarly, regarding facilities and infrastructure, with UKT as an example, basically, the database owned by UPI, can take ISO report data [23]. Mapping can be conducted with this database, for example, the submission of needs should be based on value assessment. To achieve this, the database system for facilities and infrastructure needs a support system developed to disseminate the lower level [14].
The policy is poorly understood at the user level, therefore,in the future the research findings will further clarify the targets of all policies relating to areas under the database jurisdiction (performance indicators) [24]. Data can be obtained from each faculty and can also be thought of as a Multisite campus [25] used to develop a modern campus. It is possible that other campuses imitate UPI. Regardless of this, Multisite campus [18] can be done by mapping the competence of excellence in each campus area, (source reference Data source international university). For example Base in Sonkla, regional needs site [5].
The Vice Rector for Human Resources explains that assessment centers should be kept in SPM, but its inputs and references can be from recommendation associated with this research with the report stored in the form of a database [13]. This is similar to the expertise folder that comprises of UPI, because this digital data will be the basis for making the reports in the field. From the above research findings, the communication management policy model of HR will then be implemented with regards to the Value Chain [21] model above. The important aspect of it is the number of duty that will be implemented by the human resources while carrying out their duties from:
- Recruitment of CPNS, prospective civil servants and their establishment in UPI.
- Lecturer Remuneration, activity from the beginning of the recruitment stage to its result determination stage.
- Pension Lecturer, Activity of pension management process for lecturer in Directorate of Human Resources Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia.
In addition to the above main tasks, there are also supporting duties, which include:
- Administration, Activity in administrative management within the organization that promotes main activities related to the administration as well as recording in the maintenance of infrastructure, facilities, and infrastructure of UPI Directorate of Human Resources.
- Finance, Activities in financial management within the organization that supports the main activities related to cash inflow, cash outflow and investment and funding maintenance infrastructure, facilities and infrastructure Directorate of Human Resources UPI.
- Facilities and infrastructure, activities to provide support in the form of services for all parts of the Directorate of Human Resources UPI and manage and improve infrastructure, facilities, and infrastructure.
4.3. Modeling Functions of Business Directorate of Human Resources in UPI
Modeling business functions with organizational units will be further illustrated using business models. This can be built in the form of component interaction with the organizational unit by describing each task, as displayed in the picture[26]. From the flow diagram developed above, a minimal main task is performed by the unit associated with measurable tasks [27],[28] as shown in the table below.
Table 1: Human Resources Recruitment
| No | HR Management | Description | |
| 1. | Ministry of Education | Responsible for determining the allocation of candidates needs based on employees requirements | |
| 2. |
Directorate of Hingher Education
|
Responsible for determining the allocation and specification of prospective employees needs as specified by the Ministry of National Education |
|
| 3. | Faculty/ Department | Responsible for the implementation of prospective employee recruitment activities | |
| 4. | Admission Committee | Carry out operational activities in the acceptance of prospective employees in UPI environment | |
| 5. | Prospective applicants | Register and follow the perspective stages determined by the admissions committee |
From the data and information digital results extracted, a communication management policy model is formed [27] which can be recommended from the results of research, as seen in the chart in figure 3.
5. Conclusion
From the field studies and the results obtained from analyzing the Communications “Digital Information Data” as a Policy Material Program, it can be concluded that there are some important aspects within the Directorate of Human Resources in UPI. The architectural digital-based model is developed through the instruction of new organizational structure frame work including needs fulfillment, placement, development, service, career support, remuneration, and preparation. The development of value chain pattern aimed at supporting the main tasks of Human Resources to extract data and information orientation stored in the form of physical and semi-digital data, expected to sustain the quality of policy. The design of the flow diagram model for each task is still in the adjustment stage along with new policies that require further refinement. There are at least five groups of flow diagrams to be developed including those of acceptance, placement, career development, remuneration, and retirement.
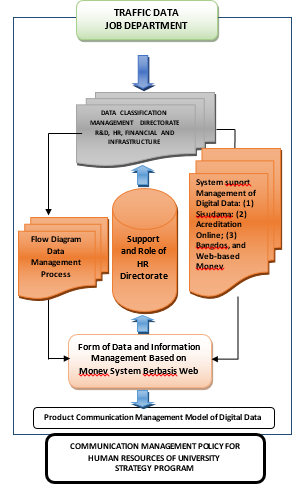 Figure 3: Communication Management Model of Policy Strategic Program Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia in Human Resources
Figure 3: Communication Management Model of Policy Strategic Program Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia in Human Resources
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgment
This work was conducted with research funding University Grant of Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia with grant on July, 2018.
- B. of Trustees,”Annual Budget Work Plan Guidelines for 2016 of Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia”, Board of Trustees, 2016.
- D. Darmawan, H. Kartawinata, and W. Astorina, “Development of Web-Based Electronic Learning System (WELS) in Improving the Effectiveness of the Study at Vocational High School ‘ Dharma Nusantara”, 14(4),pp.562-573, 2018, DOI : 10.3844/jcssp.2018.562.573
- B. of Trustees, “Strategic Plan 2016-2020 of Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia. Bandung: Board of Trustees”, 2016.
- J. Clemmer “Communication Strategy in Education”, 2012
- Suryadi, E and Darmawan, D, “Communication Management of Digital Information Data In The Field Of Human Resources As A Policy Making Resource of University Strategic Program,” pp. 1–7, 2017.
- W. Bridges, “Managing Transitions: Managing Transitions: Overcoming the Tiring Transition of Organizations”, PT. Bhuana Ilmu Populer, 2002.
- L. T. Hunger, D.J & Wheelen, “Strategic Management”,2003.
- G. Scott, M, “Principles of Management Information Systems”, 2011.
- C. Consalvo, M & Ess, The Handbook of Internet Studies,” 2011.
- U. G. Mada and U. A. Dahlan, “Resource Management And Conversion Process In Multi-Format Distributed World Web3d Framework,” 97(4), pp. 1129–1145, 2019.
- R. Buchingham, D & Willet, “Digital Generation: Child, Young People, and New Media”, Lawrence Erlbaum, 2006.
- F. Michard, T. J. Gan, and H. Kehlet, “Digital innovations and emerging technologies for enhanced recovery programmes,” Br. J. Anaesth., 119(1), 31–39, 2017.
- L. U. Khan, “Visible light communication: applications , architecture , standardization and, Digit. Communication. Networks”, 3(2), pp.78–88, 2017.
- S. Illingworth, “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology Delivering effective science communication: advice from a professional science communicator,” Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., 70 (3),pp.10–16, 2017.
- F. Beer, “Communication Strategy”, Prentice Hall Company,2013.
- M. B. Miles, A. M. Huberman, and J. Saldaña, “Qualitative Data Analysis”, 1993
- I. Indu, P. M. R. Anand, and V. Bhaskar, “Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal Identity and access management in cloud environment: Mechanisms and challenges,” Eng. Sci. Technol. an Int. J., 21(4),pp.574–588, 2018.
- E. E. H. Doyle, D. M. Johnston, R. Smith, and D. Paton, “International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction Communicating model uncertainty for natural hazards: A qualitative systematic thematic review”, Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct., 33(10),pp. 449–476, 2019.
- M.W.A. of UPI, “Strategic Plan of Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia”, UPI Press, 2015.
- U. Stikubank and N. Sciences, “Multi-Layer Framework For Security And Privacy Based Risk Evaluation On”, 97(5), pp. 1423–1433, 2019.
- K. Hersey, P & Blancshard, “Management of Organizational Behavior: Utilization of Human Resources”, Erlangga, 1982.
- D. M. Grunig, J.E., Grunig, L.A. & Dozier, “Excellent Public Relations and Effective Organisations, Mahwah”, Lawrence Erlbaum, 2002.
- UNESCO, “Education Strategic in Higher Education for Dynamic Community in the World”, UNESCO Officer Research, 2009.
- Directorate. of ICT, “Report of ICT Directorate of UPI in 2010: Information Communication Technology Directorate of Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia”, 2010.
- G. Gaither, “Multicampus System: Perspectives on Practice and Prospects”, Stylus Publishing, LLC , 1999.
- Sukarni, “Study of Communication Theory in Organizations”, 2012.
- R. E. Jack and P. G. Schyns, “Review The Human Face as a Dynamic Tool for Social Communication, Curriculum Bio l”., 14(34), 2015.
- S. K. Das, “Mobility Management — A personal perspective”, 131(1), pp.26–31, 2018.
